Figure 3. Projected working models of transcription factors (TFs) acting cooperatively with architectural proteins in T cell genome organization.
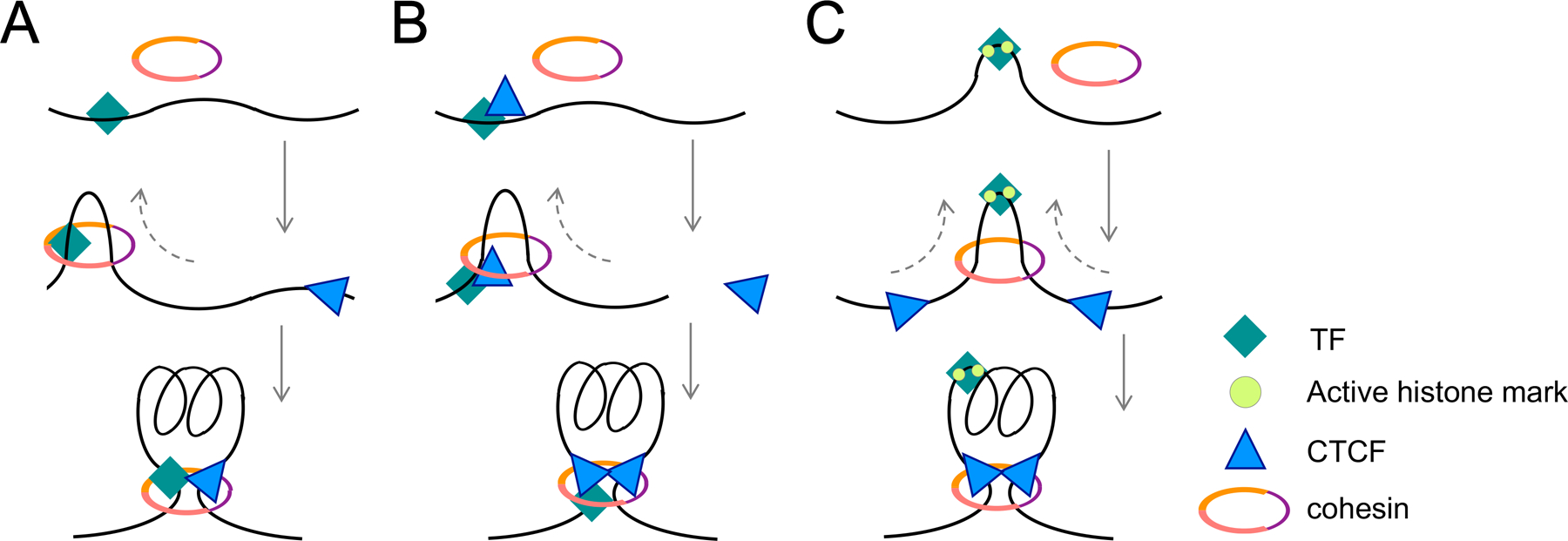
T lineage-specific TFs bind to specific DNA sequences and create nucleosome-free elements. Taking Tcf1 as an example, Tcf1 may act alone based on its intrinsic architectural function (A) or recruit CTCF (B) to assist loading of cohesin complex, which then extrudes DNA till encountering the other boundary-demarcating CTCF on the genome. TFs including Tcf1 facilitate chromatin opening and deposit of active histone marks; coupled with the DNA-bending effect by the HMG domain, Tcf1-bound enhancer elements may contribute to cohesin loading, and the ensuing symmetrical extrusion forms chromatin loops (C). Dotted arrows denote extrusion direction.
