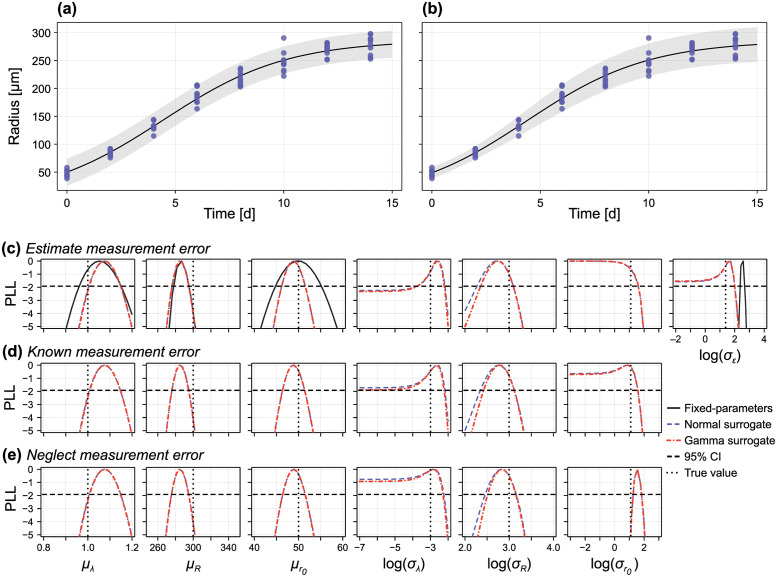
Fig 3. Profile likelihood analysis for logistic model with random parameters.
We perform inference on a synthetic data set comprising N = 10 measurements at t = 0, 2, 4, …, 14 of the random parameter logistic model (i.e., 80 independent measurements). In (C) we treat the standard deviation of the measurement noise, σε as unknown, in (D) we assume σε is known (for example, pre-estimated), and in (E) we work with a misspecified model where we assume σε = 0, corresponding to a scenario where we assume all variability in the data is due to variability in mechanistic parameters. In (C–E) we compare profiles produced using a normal surrogate model (blue dashed) and gamma surrogate model (red dotted). In (C) we also take a standard inference approach, assuming that observations are normally distributed about model predictions and where parameter variability is neglected (the fixed parameter model). In (A,B) we show the data (blue), model mean (black) and 95% prediction interval at the MLE using (A) the fixed parameter model, and (B) the random parameter approach with a gamma surrogate. Also shown are the true parameter values (black vertical dotted) and a 95% confidence interval threshold (black horizontal dashed).