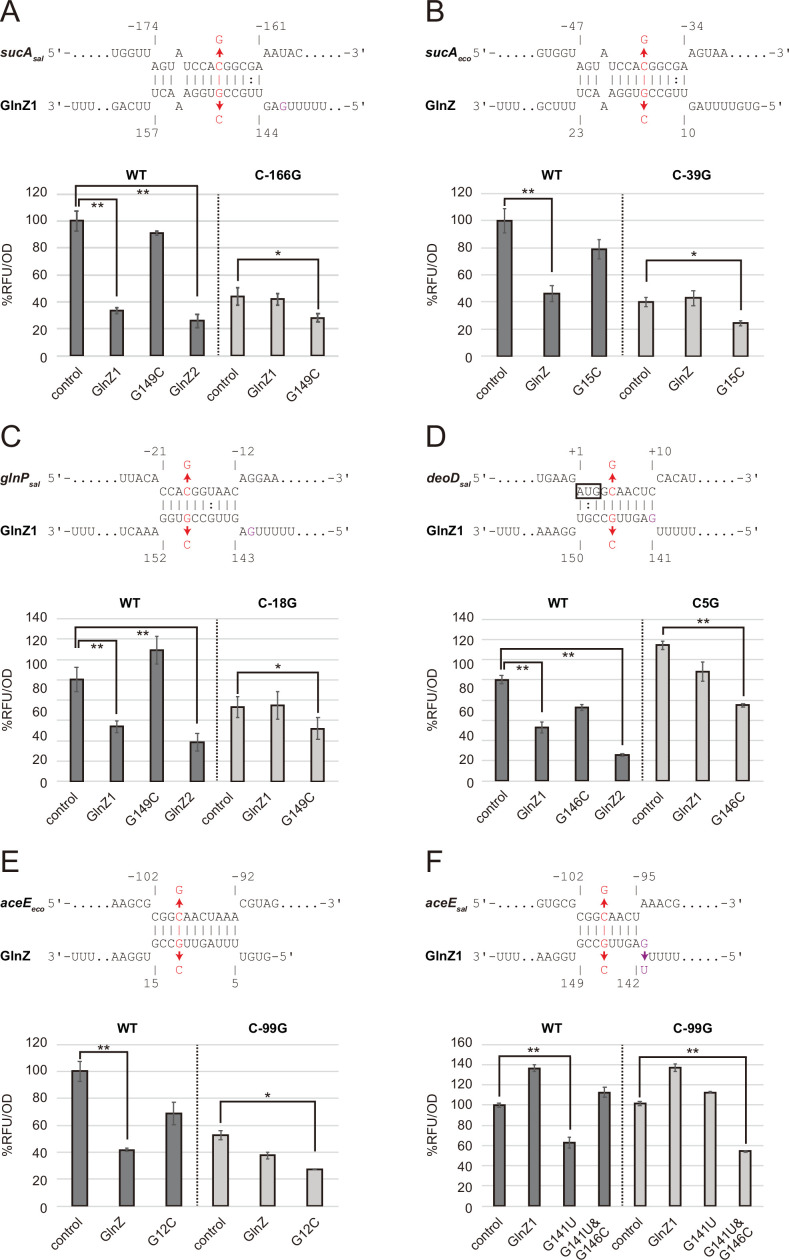
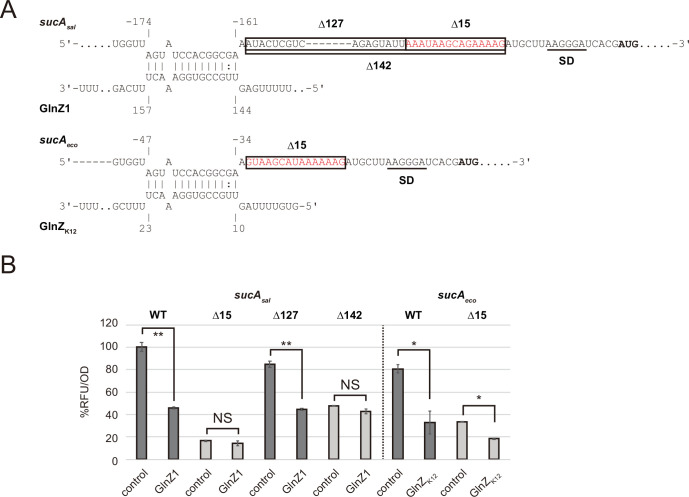
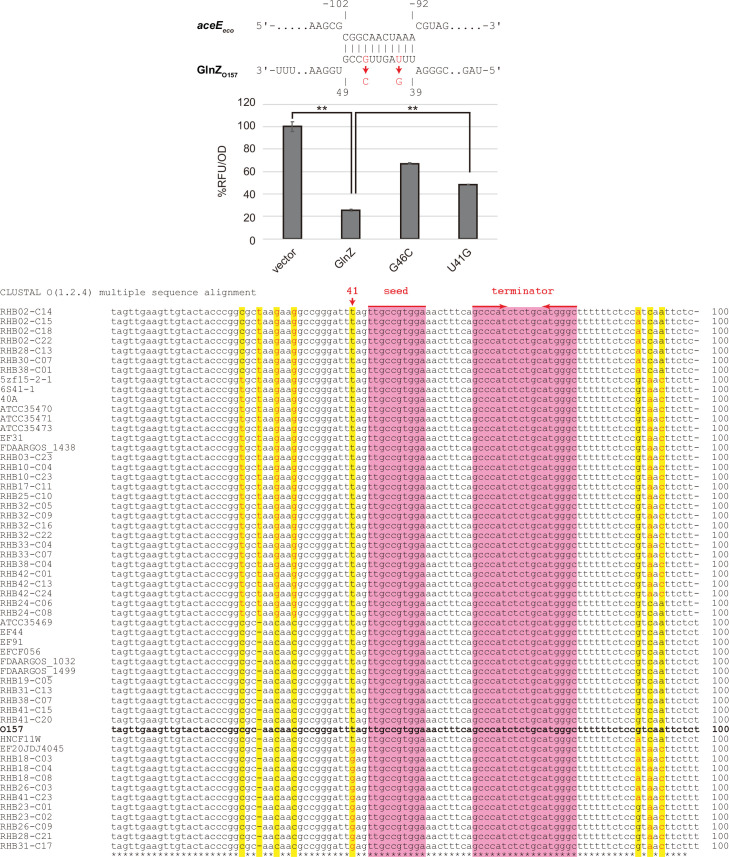
Figure 3. Post-transcriptional regulation mediated by Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli GlnZ.
Predicted interactions of GlnZ with the target mRNAs are shown in the panels, (A) S. enterica sucA, (B) E. coli sucA, (C) S. enterica glnP, (D) S. enterica deoD, (E) E. coli aceE, and (F) S. enterica aceE. The nucleotide numbers relative to the start codon of the target mRNA and the stop codon of glnA are shown above and below the nucleotide sequences, respectively. The mutated nucleotides are indicated in red, and the extra G nucleotide found in Salmonella GlnZ1 is shown in purple. E. coli ΔglnZ strain was transformed by GFP translational fusion plasmids along with pJV300 control vector or GlnZ expression plasmids (Supplementary file 5-7). Mean relative fluorescence units (RFU) normalized by OD600 calculated from biological replicates (n>3) are presented with standard deviation in percentage relative to the vector control. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and denoted as follows: **p<0.005, *p<0.05.