Fig. 1.
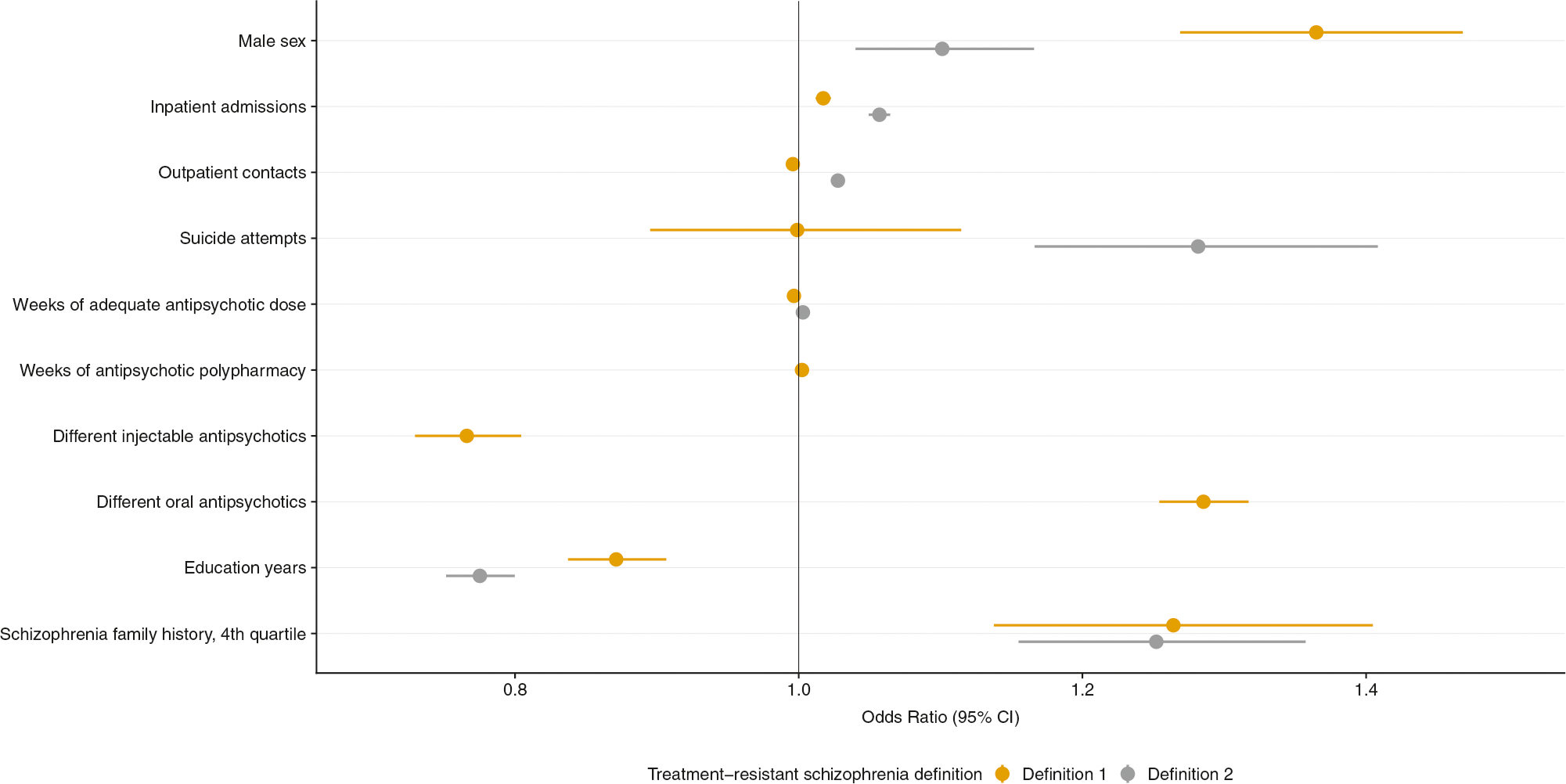
Multivariable logistic regression analyses of clinical and demographic factors associated with treatment-resistant schizophrenia within a Swedish National population-based sample (n = 23,066). The outcome is either treatment-resistant schizophrenia Definition 1 (clozapine) or Definition 2 (clozapine or polypharmacy). Results are presented as a single multivariable logistic regression model including all covariates listed and age, major depressive disorder, and substance use disorder. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CI) are reported. All factors are significantly associated with increased risk of treatment-resistance in schizophrenia (P ≤ 0.005), apart from suicide attempts with treatment-resistant schizophrenia Definition 1. This figure visualises the content of Supplementary Table S3 (Model 1)
