Fig. 2.
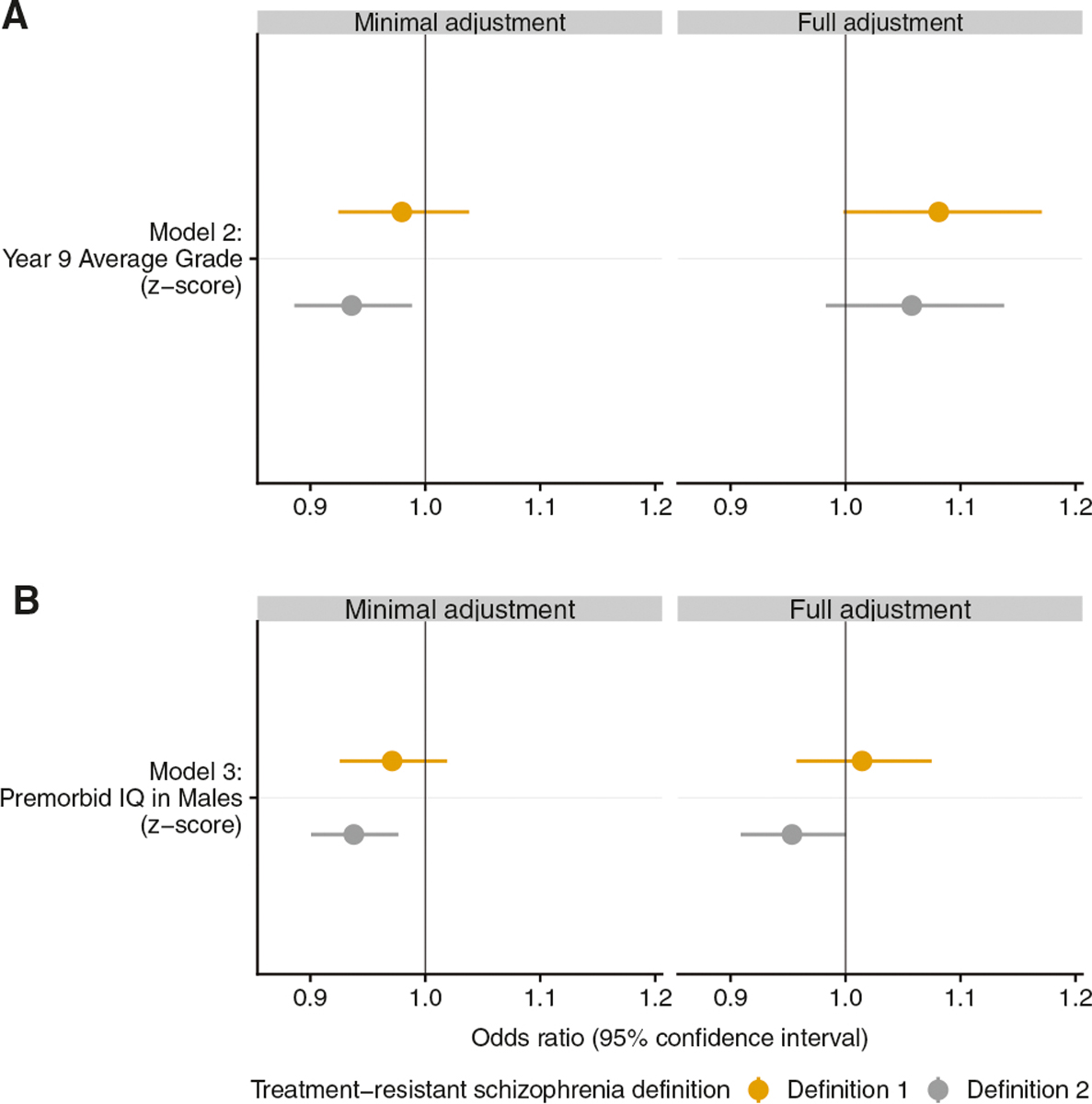
Multivariable logistic regression analyses of cognitive measures associated with treatment-resistant schizophrenia within a Swedish National population-based sample. Model 2 includes the exposure year 9 grades (minimal adjustment n = 3989, full adjustment n = 3960) and model 3 includes premorbid IQ in males (minimal adjustment n = 8238, full adjustment n = 8217). Minimal adjustment includes only the exposure of interest, whereas full adjustment includes all relevant clinical and demographic predictors (Psychiatric treatment contacts, psychiatric comorbidities, antipsychotic usage, education years, and SCZ family history score). The outcome is either treatment-resistant schizophrenia Definition 1 (clozapine) or Definition 2 (clozapine or polypharmacy). Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CI) are reported. This figure visualises the content of Supplementary Table S3 (Models 2 and 3)
