Fig. 3.
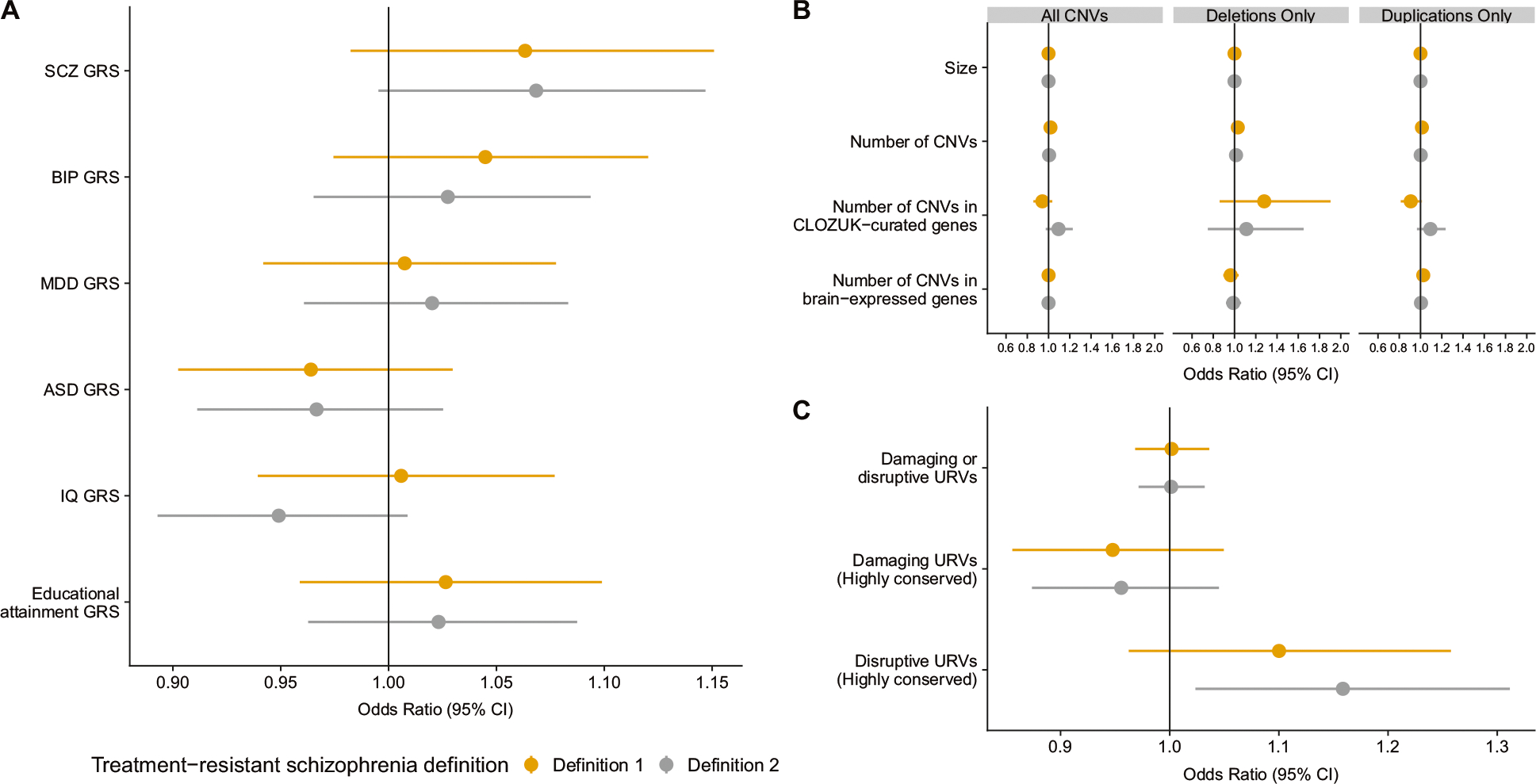
Multivariable logistic regression analyses using a genetic scores, b copy number variant measures (CNV), and c exome burden measures in association with treatment-resistant in schizophrenia (n = 4936). Panel a includes all six genetic risk scores (GRS): schizophrenia (SCZ), bipolar disorder (BIP), major depressive disorder (MDD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), IQ, and educational attainment. Panel b includes three separate models of rare CNV measures: (1) by total number of CNVs, (2) total deletions, and (3) total duplications. Panel c includes three measures of ultra-rare variant (URVs) burden measures in one model. Each model is adjusted for the first five-ancestry principal components, with panel c additionally adjusted for the count of synonymous variants. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CI) are reported. No factors were significantly associated with treatment-resistance in schizophrenia (P > 0.005). This figure visualises the content of Supplementary Table S5
