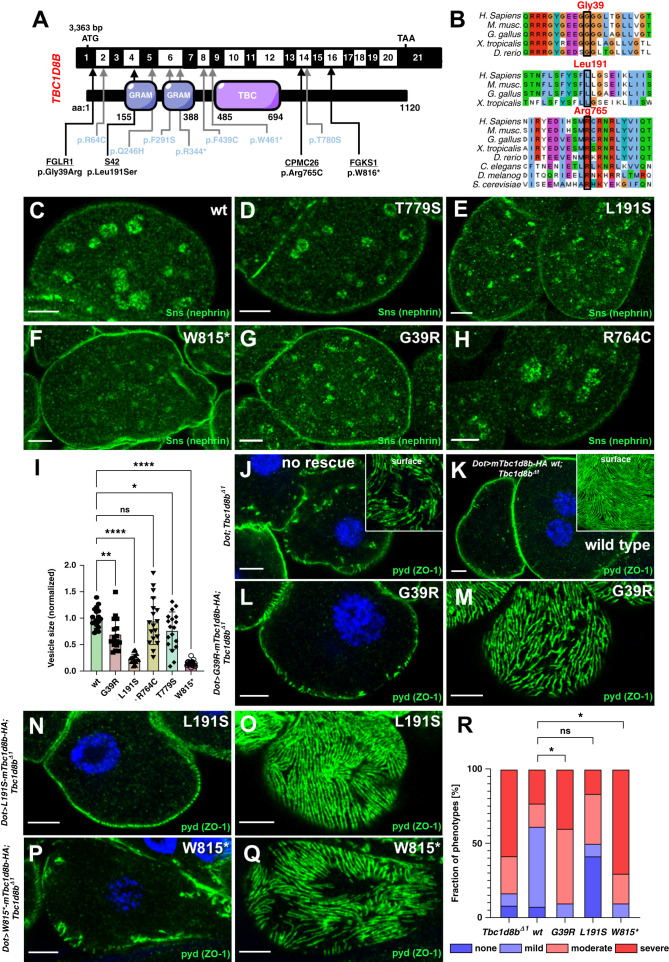
Figure 8.
Identification of novel variants in TBC1D8B in patients with FSGS and functional validation in Drosophila. (A) Schematic of TBC1D8B cDNA with the corresponding protein, including its functional domains. Arrows indicate the position of four novel variants of TBC1D8B discovered by whole exome sequencing within an FSGS cohort (black letters) together with the known variants (blue letters). (B) Alignment of amino-acid sequence of TBC1D8B protein for the indicated species illustrates level of evolutionary conservation for residues Gly39, Leu191, and Arg765. (C)–(H) Confocal microscopy images of nephrocytes stained for the ortholog of nephrin are shown. Animals express wild-type (C) or several mutant variants of mTbc1d8b carrying a C-terminal HA-tag reflecting patient-derived variants under pros-GAL4 at 31°C (D)–(H). Nephrin vesicles appear smaller for all mutant transgene except R764C. Variant T779S was previously validated (Kampf et al.).7 Note that variants are numbered according to mTbc1d8b (longest isoform) and thus may deviate from the corresponding residue in human TBC1D8B. (I) Quantitation of results analogous to (C)–(H) expressed as two-dimensional vesicle size normalized to the average of wild-type mTbc1b8 for individual cells are shown for the indicated genotypes (mean of area of the five largest vesicles±SD, n=7–10 animals per genotype, P<0.05 for T779S, P<0.01 for G39R, P<0.0001 for L191S, P>0.05 for R764C, and P<0.0001 for W815*). This indicates that nephrin (Sns) vesicles become smaller for mutants of TBC1D8B associated with FSGS with the exception of R765C. Analysis was performed in a blinded fashion. (J)–(Q) Shown are confocal microscopy images of nephrocytes stained for slit diaphragm protein pyd (ZO1) that carry the Tbc1d8b null allele together with Dorothy-GAL4 for expression of UAS transgenes. Without a UAS construct to express murine Tbc1d8b, the typical Tbc1d8b-associated phenotype with mislocalization of pyd can be observed (J), whereas expression of wild-type murine Tbc1d8b rescues this phenotypic defect (K). Tangential (M), (O), and (Q) or cross-sectional images (L), (N), and (P) of nephrocytes expressing murine Tbc1d8b variants reflecting the indicated patient-derived variants show only a partial rescue for variant G39R (L) and (M), and W815* (P) and (Q). In contrast, the expression of L191S (N) and (O) retains a substantial ability to rescue. (R) Quantitation of results analogous to (J)–(Q) expressed as percentage of animals categorized for phenotypic severity are shown for the indicated genotypes (n=10–13 animals per genotype, P<0.05 for G39R, P>0.05 for L191S, P>0.05 for R764C, and P<0.05 for W815*). Categorization was performed in a blinded fashion. For the statistical analysis using the chi-squared test, the categories were simplified to mild versus severe phenotype. This indicates that two variants (G39R and W815*) significantly lack the ability to rescue.