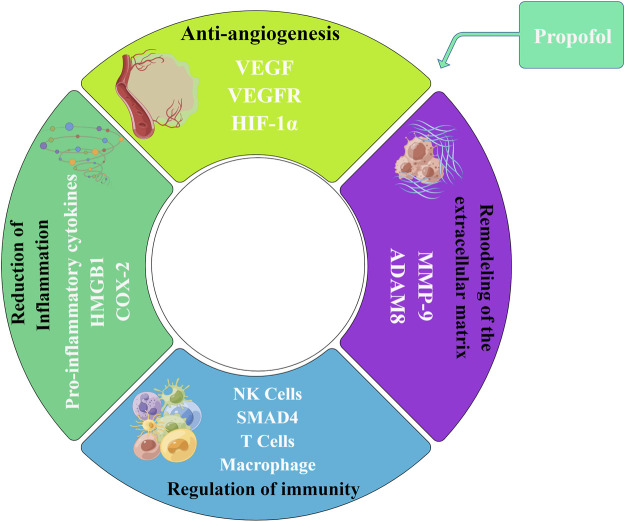
FIGURE 5.
Effect of propofol on the tumor microenvironment. Propofol can play a role in reshaping the tumor microenvironment, including anti-angiogenesis, regulation of immunity, reduction of inflammation, and remodeling of the extracellular matrix, indirectly affecting the biological characteristics of tumor cells. Propofol can inhibit the expression of VEGF/VEGFR and play an anti-angiogenesis role. Propofol regulates immunity by affecting the infiltration and activity of a variety of immune cells, such as T cells, NK cells, and macrophages. Propofol can reduce inflammation via inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and targeting the expression of HMGB1 and COX-2 inflammatory proteins. In addition, propofol can target the expression of MMP-9 and ADAM8 to remodel the tumor extracellular matrix.