Figure 9.
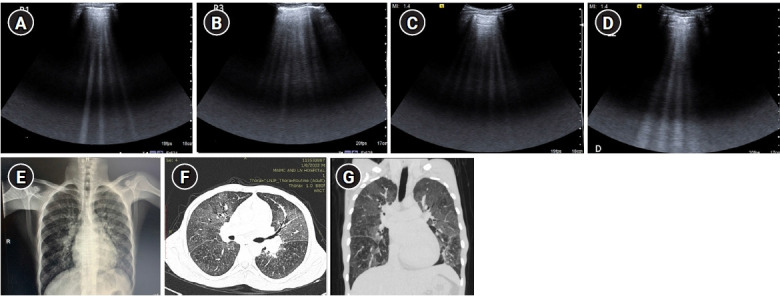
B-profile. Diffuse interstitial syndrome on ultrasound, diagnosed by the presence of multiple (≥3) B-lines in >1 scanning zone in anterolateral chest wall on each side in a patient presenting with acute dyspnea and hemoptysis. (A, B) Four B-lines are known as “septal rocket” pattern and represent interlobular septal thickening. (C, D) Five or more B-lines are called “ground glass rocket” patterns, representing ground-glass areas on the computed tomography of the chest. the pleural line in this case was regular in appearance. The patient was diagnosed with pulmonary edema based on ultrasound findings. (E) Chest X-ray revealed concordant findings in the form of cephalization of the pulmonary vasculature and prominent interstitial markings. Axial (F) and coronal (G) sections from contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography scan performed in the patient revealed ground glass opacities and Interlobular septal thickening as demonstrated by the “ground glass rocket” pattern and “septal rocket” pattern respectively on ultrasound, providing further confirmation of the diagnosis.
