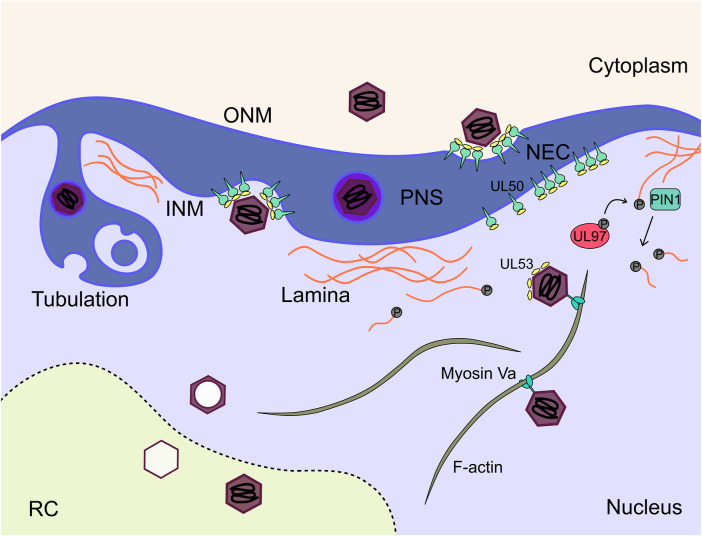
FIGURE 8.
Mature capsids traverse both nuclear membranes to enter the cytoplasm for subsequent maturation. The NEC consisting of UL50 and UL53 acts as an organisational hub on the INM to recruit host and viral proteins to facilitate this step. Additionally, the nuclear lamina poses a physical barrier for exiting capsids. The lamins are phosphorylated by the viral kinase UL97 and subsequently depolymerise. C capsids travel along nuclear actin filaments to the nuclear membrane where they undergo envelopment at the INM mediated by the NEC, and subsequent fusion with the ONM to release the nascent capsid into the cytoplasm. NEC, nuclear egress complex; INM, inner nuclear membrane; ONM, outer nuclear membrane; RC, replication compartment; PIN1, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1.