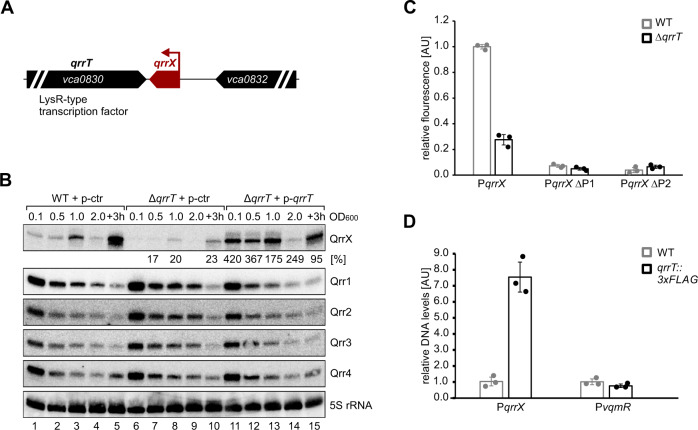
Fig. 5. Transcriptional control of qrrX.
A Schematic representation of the genomic context of qrrX. The qrrX gene is marked in red. The vca0830 gene encodes a LysR-type transcription factor (QrrT). B Role of QrrT for QrrX levels. V. cholerae wild-type and ∆qrrT cells harboring either an empty control vector or a qrrT overexpression plasmid (p-qrrT) were cultivated in LB medium and RNA samples were collected at different stages of growth. Northern blot analysis was performed to determine QrrX and Qrr1-4 levels. 5 S ribosomal RNA served as loading control. The experiment was performed with three independent biological replicates (n = 3). C Regulation of the qrrX promotor. V. cholerae wild-type and ∆qrrT cells carrying an mKate2-based transcriptional reporter for qrrX (PqrrX::mKate2) or a mutated version (PqrrX::mKate2 ∆P1 or PqrrX::mKate2 ∆P2, see Fig. S7G) were cultivated in LB medium to OD600 of 1.0 and analyzed for fluorescence. V. cholerae wild-type carrying PqrrX::mKate2 were set to 1. Bars show mean of independent biological replicates ±SD, n = 3. D ChIP analysis of QrrT. V. cholerae wild-type and qrrT::3XFLAG cells were cultivated to OD600 of 1.0 and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Bar graphs show relative levels of the qrrX and the vqmR promotors (PqrrX and PvqmR), determined by quantitative PCR and PqrrX levels in WT V. cholerae were set to 1. Data are presented as mean values of independent biological replicates ±SD, n = 3. Source Data underlying panels B–D are provided as a Source Data file.