Figure 3.
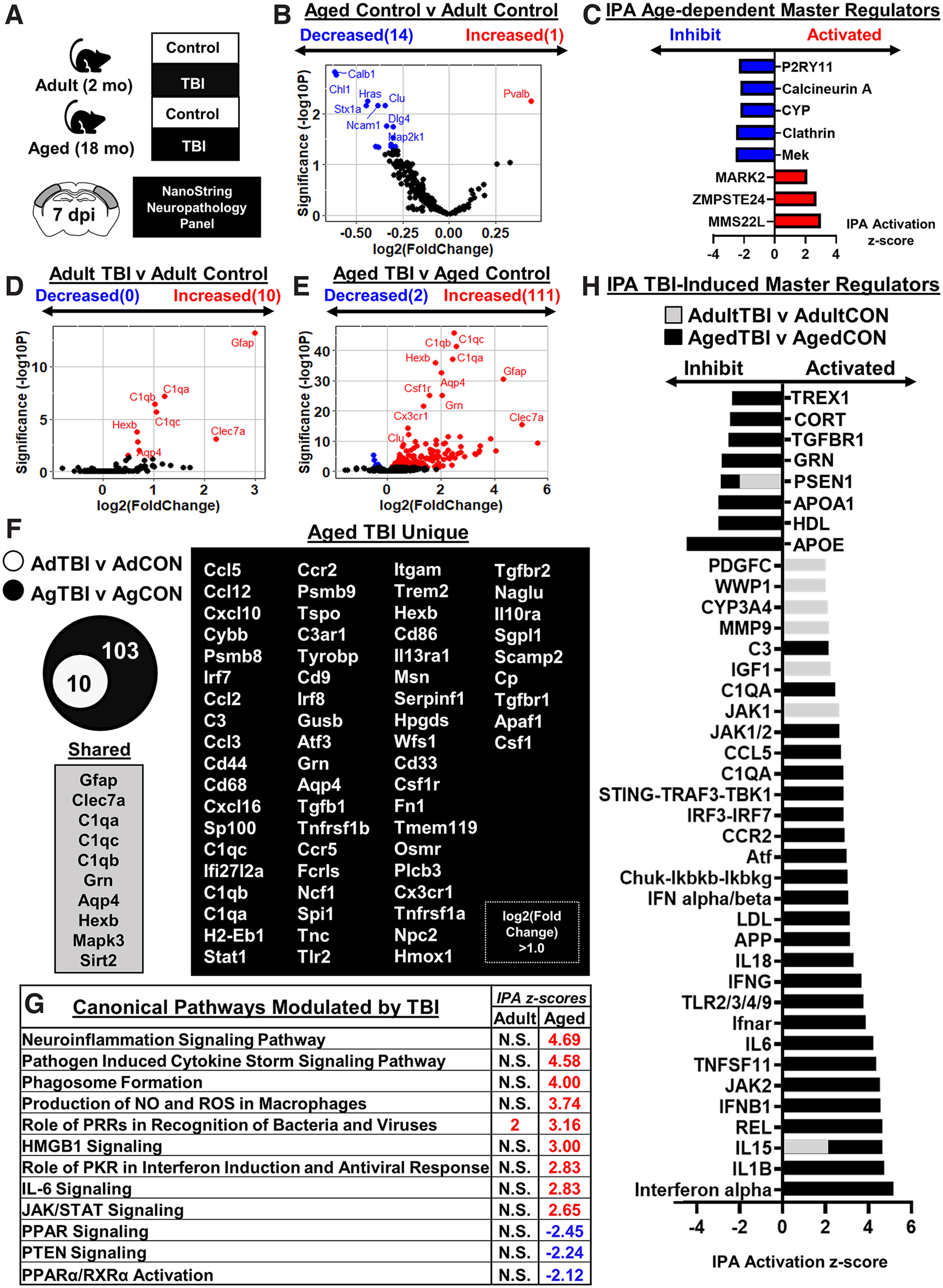
Inflammatory gene expression in adult and aged cortex 7 dpi. A, Adult (2 months of age) and aged (18 months of age) male C57BL/6 mice were subjected to midline fluid percussion injury (TBI) or left as uninjured CONs. Cortical tissue was microdissected and flash frozen at 7 dpi. RNA was collected, and mRNA copy number was determined using a NanoString nCounter Neuropathology panel (n = 3). B, Volcano plot of significantly differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05) compared between Aged-Control and Adult-Control mice. Genes in red were increased with age, and genes in blue were decreased with age. C, IPA of canonical pathways compared between Aged-Control and Adult-Control mice. Positive z score indicates activated and negative z score indicates inhibited in Aged-Control versus Adult-Control mice. D, E, Volcano plots of significantly differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05) compared between Adult-TBI and Adult-Control mice (42 genes; D) and Aged-TBI and Aged-Control mice (242 genes; E). Genes in red were increased, and genes in blue were decreased by TBI in each age group. F, Venn diagram of significantly differentially expressed genes in the Adult-TBI versus Adult-Control and Aged-TBI versus Aged-Control comparison. Genes were grouped as follows: (1) unique to Adult-TBI (6 genes), (2) shared between TBI groups (36 genes), and (3) unique to Aged-TBI (206 genes). G, IPA of significant canonical pathways (z score) activated or inhibited by TBI in adult and aged mice. N.S. denotes IPA canonical pathways that are not significantly activated. H, IPA of significant master regulators (z score) activated or inhibited by TBI for both adult mice (gray bars) and aged mice (black bars). Adult (gray) bars were overlapped on top of the aged (black) bars.
