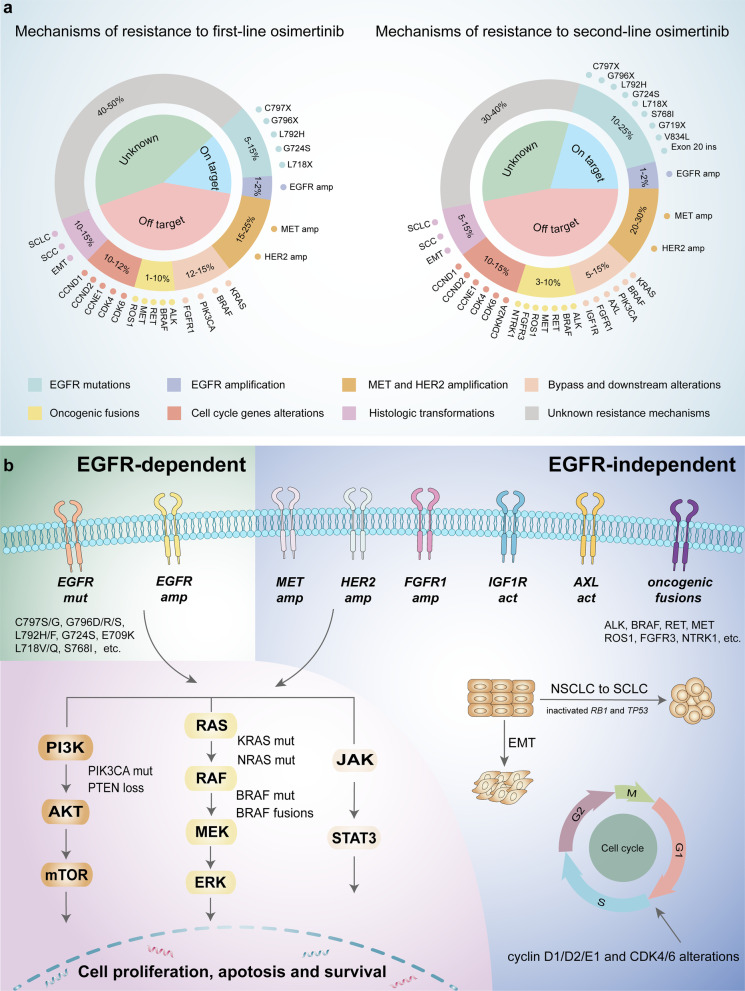
Fig. 2.
Mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib. a Resistance mechanisms of osimertinib occur in first-line (left) and second-line therapy (right), and incidences of each class of resistance mechanisms are also presented. b Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib are broadly divided into EGFR-dependent and EGFR-independent resistance mechanisms. The latter include bypass signaling activation, oncogenic fusions, downstream pathway alterations, histologic transformations and cell cycle gene alterations. Abbreviations: act, activation; amp, amplification; mut, mutation