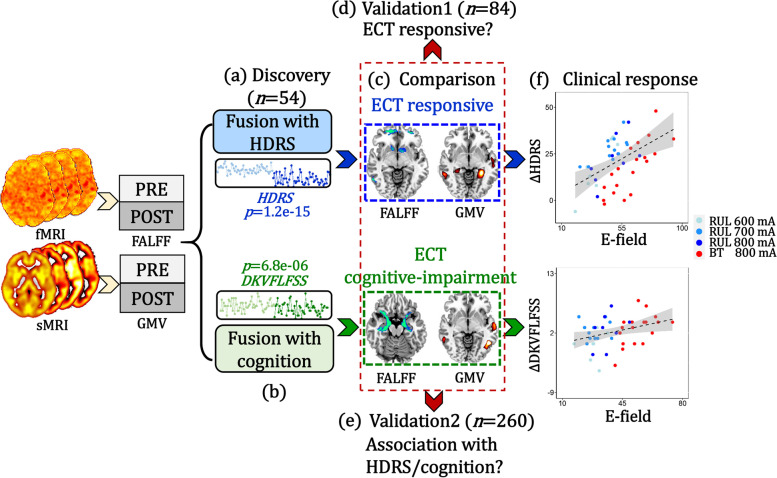
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the study design. a HDRS-guided fusion was performed on fALFF+GMV to identify ECT antidepressant-response multimodal brain network. b DKVFLFSS-guided fusion was performed on fALFF+GMV to identify ECT cognitive-impairment multimodal brain network. The p-values in a–b represent the longitudinal group difference of HDRS and DKVFLFSS. c Comparisons between antidepressant-response and cognitive-impairment networks identified common and specific regions between these two networks. d Linear projection projected the identified antidepressant-response and cognitive-impairment components onto an independent second ECT dataset for validation (n = 84). e Averaged fALFF/GMV was calculated within the common areas between antidepressant-response and cognitive-impairment networks to test whether the common regions are associated with depression severity/cognition with a third independent dataset (n = 260). f The associations between the ECT-induced E-field within these two networks and clinical responses were assessed. g Optimal pulse amplitude was estimated based on receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for both antidepressant and cognitive impairment networks