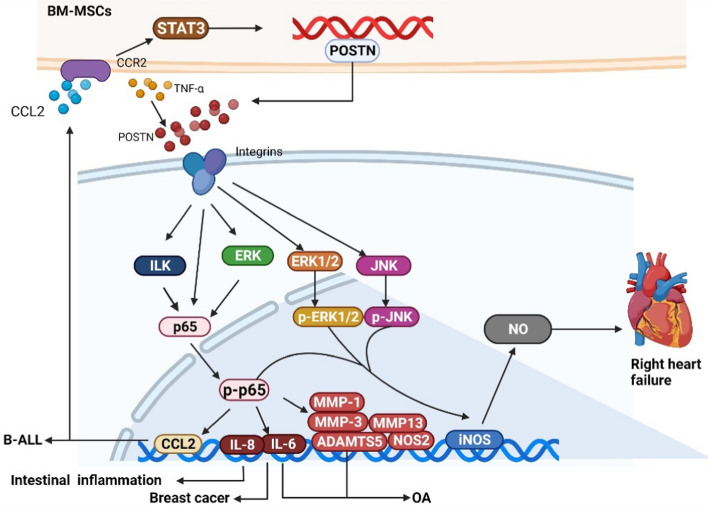
Fig. 4.
POSTN can activate the NF-κB pathway to participate in cancer and inflammatory diseases. (1) rPOSTN can upregulate the expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, IL-6, IL-8, NOS2, and ADAMTS5 by inducing the phosphorylation of p65 to promote OA. (2) TNF-α can increase the expression of POSTN in intestinal epithelial cells, while the mRNA level of IL-8 and the activity of NF-κB were significantly increased under the upregulation of POSTN and TNF-α. (3) rPOSTN can increase the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-κB in RVFbs, where increased iNOS expression and subsequent NO production eventually induced right heart failure. (4) POSTN secreted by BM-MSCs can activate the integrin/ILK/NF-κB pathway to promote B-ALL cells’ expression of CCL2, which, in turn, upregulates the POSTN level of BM-MSCs by activating STAT3 through CCR2 binding, eventually leading to the progression of B-ALL. (5) POSTN can increase the level of IL-6 and IL-8, mediated by the NF-κB pathway while maintaining the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer stem cells, among which the ERK pathway acts upstream of NF-κB