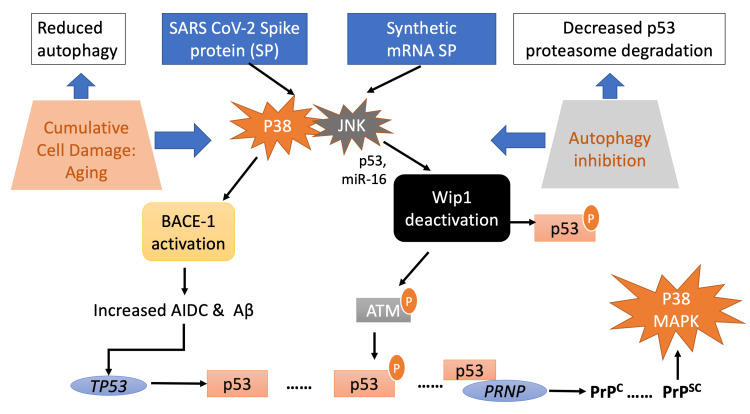
Figure 2. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein neurotoxicity dependence on age and inhibition of autophagy.
The ability to induce autophagy is age dependent. Autophagy is inhibited in part through DNA damage to the sequestosome p62 promoter, caused by oxidative stress. The activation of p38 MAPK and JNK pathways by the spike protein in nerve cells leads to BACE-1 activation and, through JNK-mediated Wip1 deactivation, increases activated (phosphorylated) p53. The release of AIDC via APP metabolism further enhances TP53 transcriptional activation and hence p53 expression. Free P53 can be further phosphorylated by ATM (being active through JNK-dependent microRNA-16 Wip1 inhibition). The overall process leads to the accumulation of levels and expression of PrPC. Conformational alteration of PrPC to PrPSC induces the activation of p38 MAPK, constituting the whole age-dependent process. Adapted from: Refs. [12, 15, 94, 112, 115, 118, 127-128, 131, 133, 143].