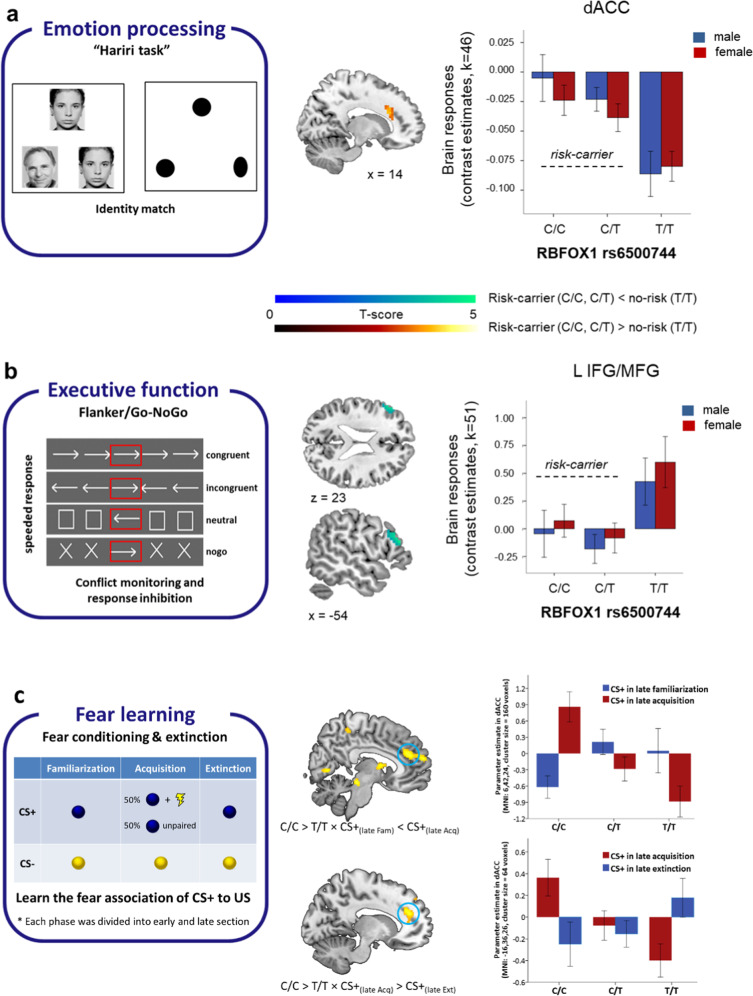
Fig. 2. Effects of the rs6500744 RBFOX1 genotype on brain responses during implicit emotion processing and executive functioning in healthy adults, and on fear learning in patients with panic disorder and agoraphobia.
A left panel: Schematic overview of the face matching task. Participants had to select either one of the two faces or forms shown at the bottom of the screen that was identical to the target stimulus shown at the top of the screen. A right panel: C-allele carrier (C/C and C/T) showed increased brain responses in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) compared to those with the T/T genotype during matching faces vs. forms (faces > forms; MNI coordinate: x = 15, y = 23, z = 27, peak-voxel family-wise error-corrected [FWE] P = 0.010, T = 3.9 within bilateral ACC). B left panel: Schematic overview of the Flanker/Go-NoGo task. Participants had to respond to the direction of the arrow shown in the centre (red box for illustration purposes only) B right panel: C-allele carriers (C/C and C/T) showed reduced brain responses in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (L dlPFC) compared to those homozygous for the T allele during executive functioning (contrast: [incongruent & nogo] > [congruent & neutral]; MNI coordinates: x = −54, y = 32, z = 21, peak-voxel pFWE-corrected=0.039, T = 4.55, across the whole-brain). Brain maps were thresholded at p < 0.001 uncorrected for display purposes. Error bars indicate ± 1 standard error. C left panel: Schematic overview of the fear conditioning and extinction task. During the acquisition phase, 50% of CS+ was paired pseudo-randomly with the US and 50% were not. Only those trials in which no US was delivered were analysed during acquisition to avoid overlap with neuron activation directly related to the presentation of the US. C right panel: Using ROI analysis within the ACC, homozygote risk allele carriers (C/C) compared to T/T homozygotes revealed increased activation in the dACC for CS+ after fear acquisition (CS+ in the late acquisition> CS+ in the late familiarization; cluster size = 61; peak-voxel family-wise error-corrected [FWE] P = 0.014, T = 3.87), and activation reduction for CS+ after fear extinction (CS+ in the late acquisition >CS+ in the late extinction; cluster size = 11; peak-voxel family-wise error-corrected [FWE] P = 0.018, T = 3.86). Brain maps were thresholded at p < 0.001 uncorrected for display purposes. Error bars indicate ± 1 standard error.