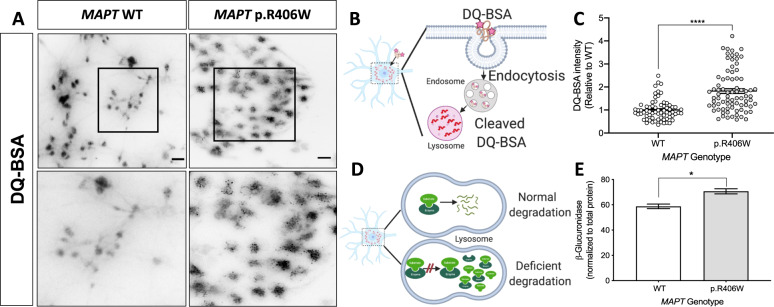
Fig. 5. Lysosomal dysfunction in human iPSC-neurons expressing the MAPT p.R406W mutation.
Human iPSC-neurons neurons from a MAPT p.R406W mutation carrier and isogenic, CRISPR/Cas9-corrected control (wild-type (WT)) were differentiated into cortical neurons and cultured for 6 weeks prior to analysis. A MAPT p.R406W neurons exhibit increased DQ-BSA fluorescence. Live cells were incubated with DQ-BSA and were imaged as described in Methods. Representative images of DQ-BSA-stained neurons are shown in gray scale for clarity. Scale bar, 10 microns. Lower panel represents magnification of the cells in the black box. B Diagram of DQ-BSA mechanism. C Quantification of the intensity of DQ-BSA staining in soma from MAPT p.R406W neurons (n = 79 cells) and isogenic controls (n = 69 cells). D Diagram of secondary elevation of lysosomal enzymes. E Enzyme activity of β-Glucuronidase measured in cell lysates from MAPT p.R406W neurons and isogenic controls. Enzymatic activity was normalized to the total protein. Graphs represent mean ± SEM. Significance was determined using an unpaired, t-test. *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001.