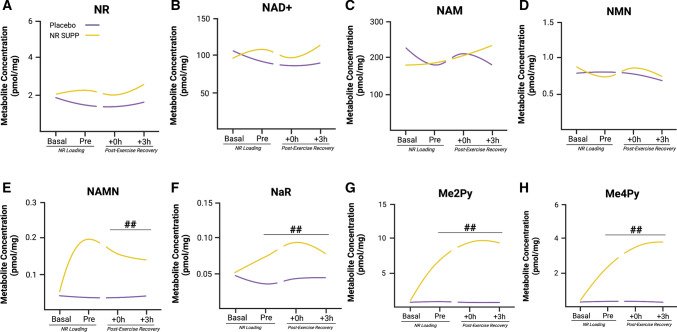
Fig. 2.
Effect of nicotinamide riboside (NR) loading and acute endurance exercise on the skeletal muscle nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) metabolome. The figure shows the effects of seven days of NR loading (NR SUPP) versus cellulose placebo on NAD+ metabolism in young male volunteers prior to an acute bout of endurance exercise. Specifically, NR loading had no effect on NR, NAD+, nicotinamide (NAM), and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) content in skeletal muscle (A–D). However, deaminated NAD+ precursor, nicotinic acid riboside (NaR), and, methylated breakdown products, N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (Me2Py) and N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide (Me4Py), were elevated following NR loading and sustained during the 3-h post-exercise period (E–G; ## denotes p < 0.05 placebo vs NR SUPP). Interestingly, the phosphoribosylated NAD+ precursor, nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NAMN), was only increased post-NR supplementation and exercise (H), whilst exercise alone had no effect on the NAD + metabolome in skeletal muscle (A–G). h hours. Image created by BioRender.com