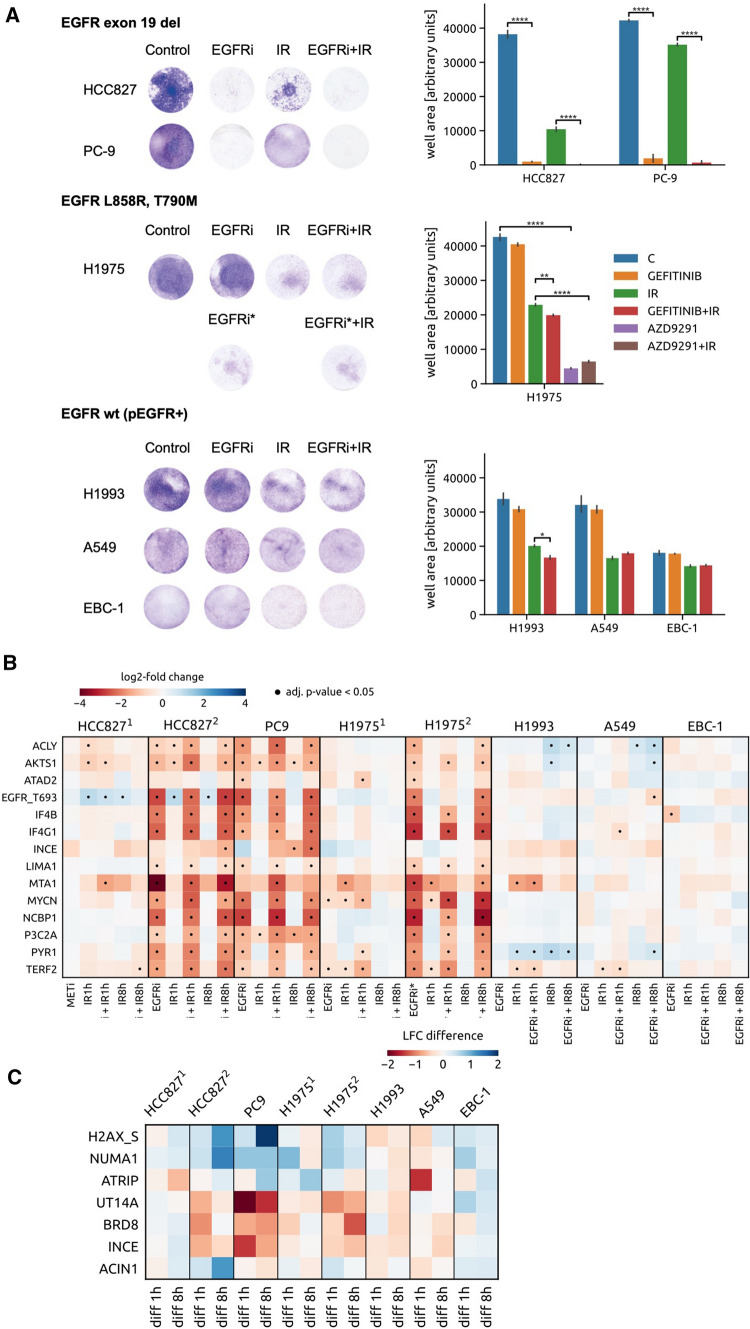
Fig. 3.
Phenotypic and protein phosphorylation responses of EGFR-positive cancer cell lines towards EGFR targeting. A Representative pictures (left) and quantification (right) of viability of a panel of EGFR-positive cells towards EGFR inhibition by gefitinib (EGFRi) or AZD9291 (EGFRi*), IR and their combination. Viability assays were performed to assess sensitivity of EGFR-positive models to EGFRi exerted by gefitinib, IR and the combinatorial treatment; pMET-positive models were exposed to METi, alone and in combination with IR, and the T790M-harboring mutation cells were exposed to third generation EGFR TKI AZD9291, alone and in combinatorial regime with IR. Statistical analysis was performed by GraphPad Prism. p values were calculated by Student t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). B Heat map displaying shared phosphorylations occurring in the EGFR-addicted systems HCC827 (HCC8272) and PC-9 upon exposure to the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib (EGFRi) and their modulation upon EGFR inhibition, IR and their combination 1 or 8 h post IR across the EGFR-positive cell line cohort. In addition to the gefitinib treatment (H19751), the H1975 cell line has been exposed also to EGFR inhibition by AZD9291 (EGFRi*; H19752). Apart of the gefitinib treatment (HCC8272), MET inhibition by tepotinib was tested in MET- and EGFR-expressing HCC827 cells (HCC8271). Blue, upregulated phosphopeptides. Red, downregulated phosphopeptides. Dot, adjusted p-value < 0.05. C Modulation of DDR-related phosphopeptides in the EGFR-positive cell line panel that were identified in MET-addicted systems as significantly differently regulated between IR and METi + IR condition (Fig. 2C). The heat map displays differences between the treatment by IR and EGFRi + IR assessed in the EGFR-positive cell line panel. To demonstrate the difference between EGFR and MET targeting, effects of the treatments including either METi or EGFRi have been assessed for the HCC827 cell line (HCC8271 and the HCC8272, respectively)