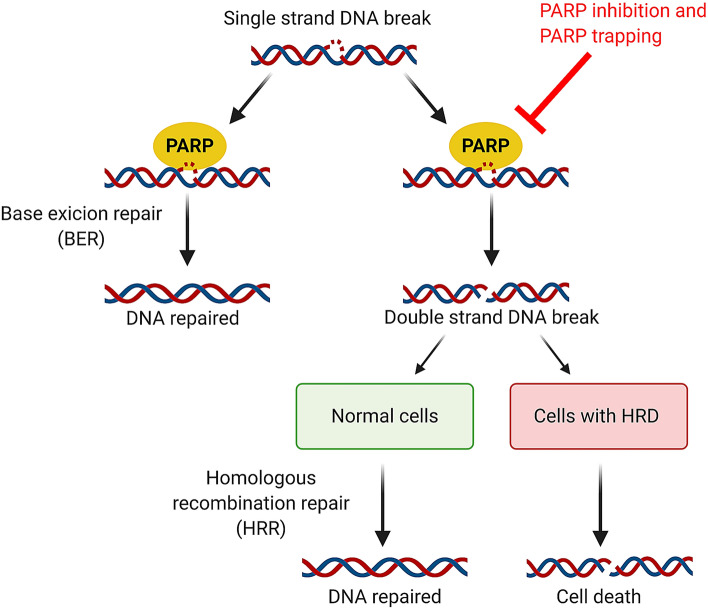
Fig. 1.
Mechanism of action of poly (ADP) ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. Single-strand breaks in DNA are repaired through base excision repair mediated by PARP enzymes. Inhibition of PARP or trapping of PARP on the DNA by PARP inhibitors, result in double-strand breaks in DNA. In normal cells harboring the homologous recombination repair mechanism, double-strand breaks are repaired and the cell survives. In cells with an homologous recombination deficiency (HRD), including breast cancer (BRCA) 1 and 2 mutations, this repair mechanism is absent leading to accumulation of double-strand breaks and cell death