Fig. 2.
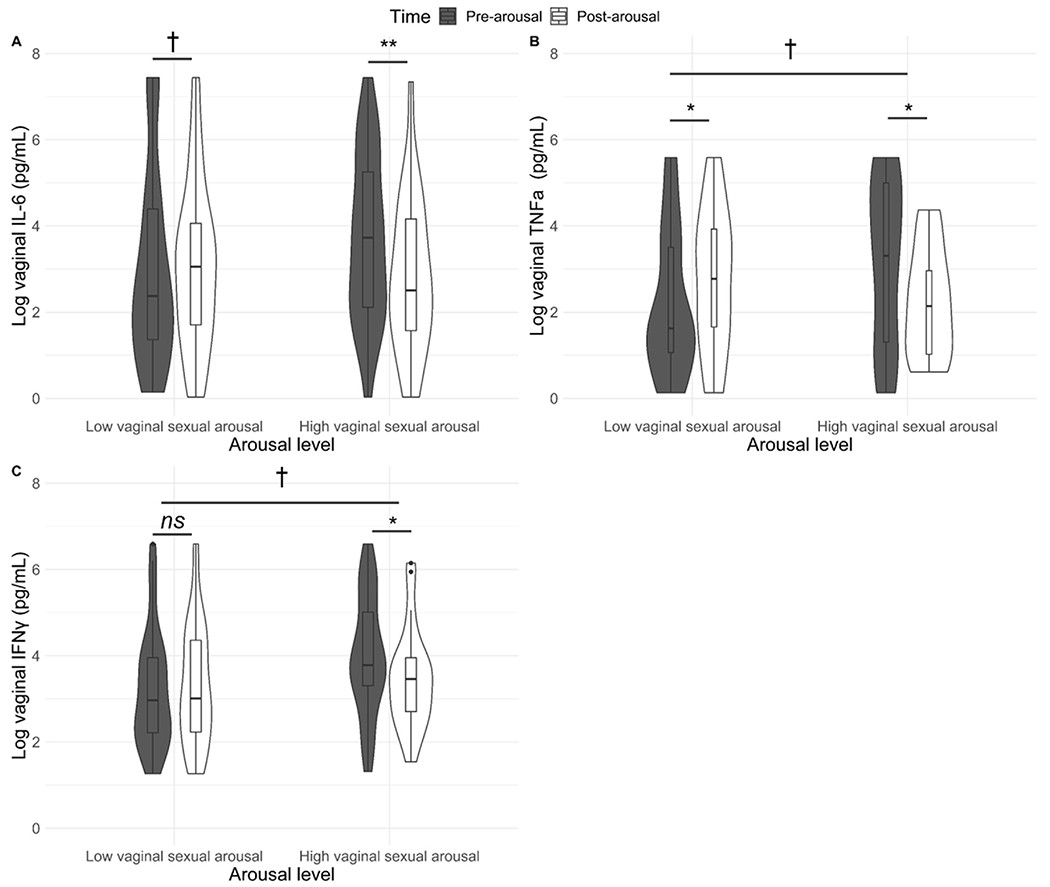
a–c. Changes in vaginal cytokines following sexual stimulation as a function of degree of vaginal sexual arousal. All values are adjusted for weight/dilution. For presentation we designated high and low arousal by median split, but analyses all used the continuous variable of percent change in vaginal pulse amplitude. Higher vaginal blood flow during sexual stimulation was associated with significant decreases in vaginal cytokines from pre- to post-arousal, while lower vaginal blood flow was associated with either no change or moderate increases in vaginal cytokines. There were marginally significant differences at the pre-arousal timepoint in vaginal TNF and IFN between women who went on to have either high or low vaginal arousal. † p < 0.1, * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.
