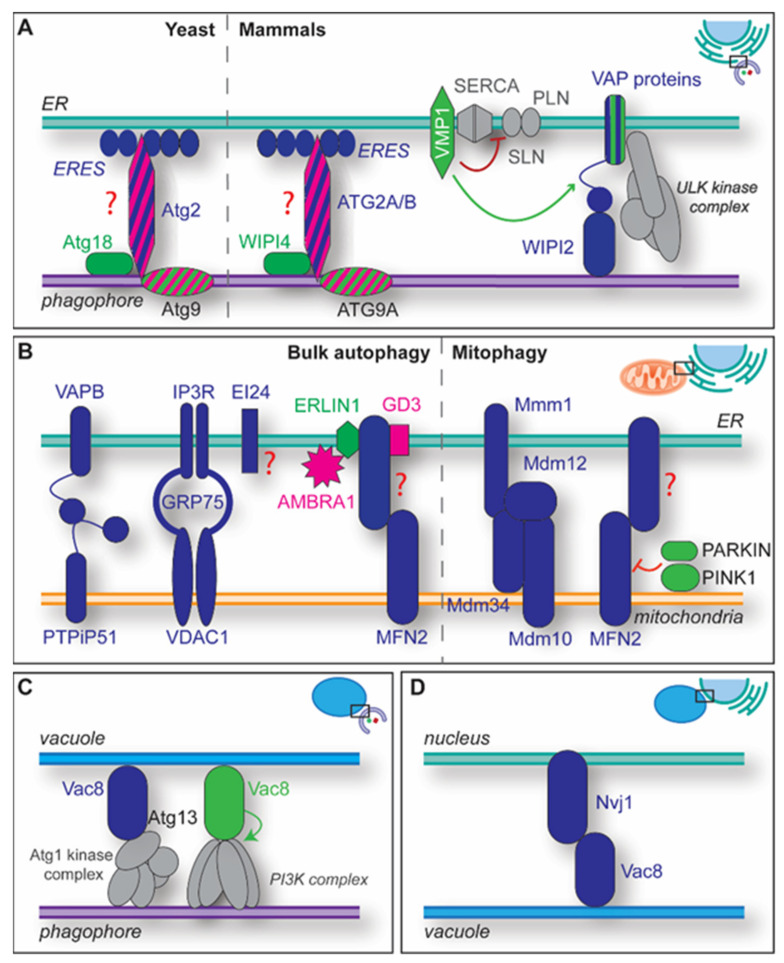
Figure 3.
Overview of some of the MCSs playing a relevant role in autophagy. (A) One type of ER-phagophore MCSs involve Atg2/ATG2A/ATG2B, Atg9/ATG9A, Atg18/WIPI4 and the ERES. The Atg2/ATG2A/ATG2B tether partner at the ERES remains to be identified, which is indicated by the red question mark. Atg2/ATG2A/ATG2B very likely supply the phagophore with lipids. In addition to probably assisting the transfer of lipids by ATG2 proteins, the VMP1 lipid scramblase exerts a regulatory role at the phagophore-ER MCSs by preventing the inactivation of the ER-localized calcium pump SERCA (red line) by PLN/SLN binding (red arrow). VMP1 also appear to be a regulator (green arrow) of MCSs between the phagophore and the ER by modulating the interaction between VAP proteins and both FIP200, which stabilizes the ULK kinase complex (grey) at the omegasome, and WIPI2. (B) ER-mitochondria MCSs and MAMs are central for autophagosome biogenesis and several of them have been described. Their interrelationship remains largely unknown, i.e., it is unclear if the different MAMs implicated in autophagy are part of the same MCSs. VAPB and PTPIP51 form one of the MAM tethers, the complex of VDAC1, IP3R and GRP75 another one. EI24 interacts with the subunits of this complex, indicated by the grey dashed lines, and is required for normal autophagic flux. However, the role of EI24 in autophagy is mechanistically not well understood, represented by the red question mark, although a very recent study connects it to calcium signaling [83]. The tether MFN2 forms complexes with GD3, its binding partner, ERLIN1, and AMBRA1 in MAM-specific lipid-microdomains, to regulate autophagosome biogenesis. ERLIN1 and GD3 are associated to lipid-rafts in the ER, and ERLIN1 and AMBRA1 interact in those. AMBRA1 is phosphorylated by ULK1 upon autophagy induction and recruits the autophagy-specific PI3K complex to the omegasome. In yeast, the ERMES formed by Mdm10, Mdm12, Mdm34 and Mmm1 are key for mitophagy progression. In mammals, during PINK1-dependent mitophagy, MFN2 tethers are disassembled through the action of PINK1 and PARKIN, indicated by the green dashed arrow, which leads to the proteasomal degradation of MFN2. (C) The vacuole-phagophore MCSs, which are involved in non-selective and selective types of autophagy in yeast, are formed by interaction of Vac8 with the Atg1 kinase complex, in particular with the Atg13 subunit. In those MCSs, Vac8 also recruits concomitantly the autophagy-specific PI3K complex via interaction with its subcomplex Vps15-Vps34 (D) The nucleus-vacuole MCSs are involved in yeast PMN and are generated by an interaction between Nvj1 and Vac8. Proteins colored in blue are tethers, proteins colored in green have a regulatory function, while the one in pink represents functional proteins. ATG complexes are in grey. Proteins striped in dual colors exert the two functions displayed by each color.