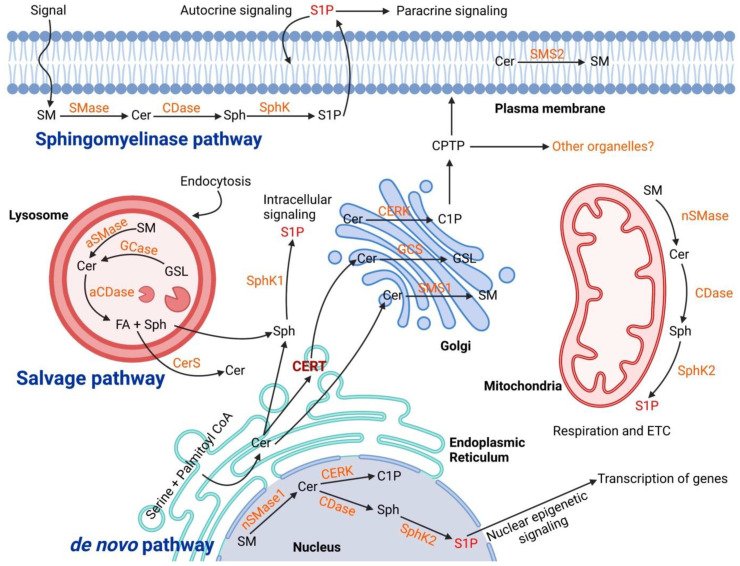
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of ceramide in cellular organelles and the complex biochemical pathways in downstream. The ceramide main synthesis routes are De novo in the Endoplasmic Reticulum, Salvage pathway in Lysosome, and Sphingomyelinase both in lysosome and plasma membrane. The transfer of ceramides to the Golgi is mediated through ceramide transfer protein (CERT) within vesicles. In the Golgi, different classes of sphingolipid are synthesized and transported to the cellular sites of action. In the plasma membrane and lysosomes, the main catabolic pathways of sphingolipids are “sphingomyelinase (SMase)” to produce ceramides. The produced ceramides go under further metabolism to generate other sphingolipid species such as sphingosine (Sph), sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) and also sphingomyelin (SM). Abbreviation: Acid Ceramidase (aCDase), Ceramidase (CDase), Ceramide Kinase (CERK), Ceramide Synthase (CerS), Glucocerebrosidase (GCase), Glucosylceramide Synthase (GCS), Glycosphingolipid (GSL), Sphingomyelin Synthase (SMS).