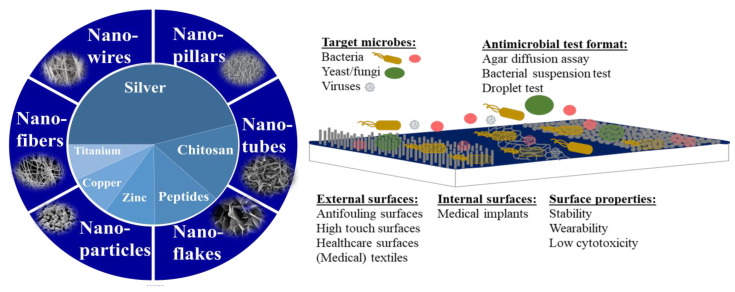
Figure 1.
Forms of antimicrobial nanomaterials and the key properties of nanomaterial-based antimicrobial surfaces. Left side: antimicrobial agents based on literature search in ISI WoS (January 2022) when out of 33,000 articles matching keywords “antimicrob* AND nano*”, 12,552 were on silver, 4400 on chitosan, 3519 on peptides, 2663 on zinc, 2272 on copper, and 1975 on titanium. The physical forms of antimicrobial nanomaterials include elongated nanostructures, such as nanofibres, -wires, -pillars, or nanotubes, nanoparticles or other structures. Right side: nanoparticle, nanopillar or nanofiber structures deposited or embedded onto antimicrobial surfaces. Common surface types, key physico-chemical properties, microbial targets, and antimicrobial testing formats are shown.