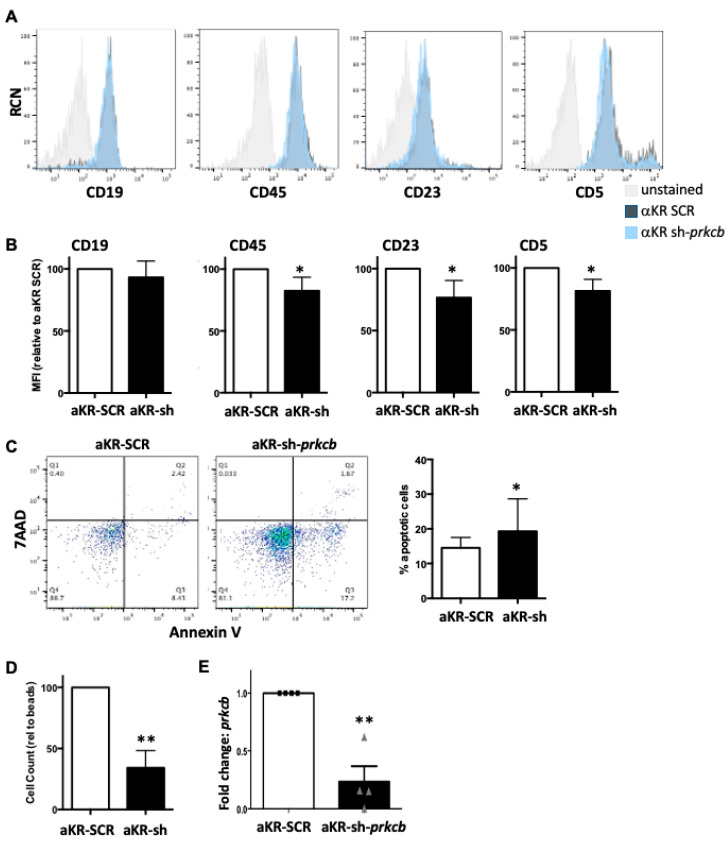
Figure 1.
Reduction in PKCβ expression inhibits the initiation of PKCα-KR-mediated CLL development. Knockdown of prkcb (or scrambled (SCR) control) was performed in HSPC cells within 24 h of isolation from the mouse, then these cells were retrovirally transduced with MIEV or PKCα-KR (αKR) at d7. Cells were co-cultured with OP9 in the presence of cytokines for up to 35 days. Phenotypic characterisation of the cells was carried out by flow cytometry analysing: (A) CD19, CD45, CD23 and CD5. Representative histogram plots are shown, gated on FSC/SSC and GFP+ cells comparing αKR sh-prkcb cells with αKR-SCR cells compared with unstained cells (gating strategy shown in Supplementary Figure S1); (B) Average MFIs of CD19, CD45, CD23 and CD5 surface markers are shown relative to αKR-SCR cultures (n = 5); (C) Apoptosis was determined by AnnV/7AAD staining. A representative dot plot shows Annexin V vs. 7AAD staining in αKR-SCR cells and αKR sh-prkcb. The graph shows the percentage apoptotic (AnnV+) cells present in cultures post d14 (n = 5); (D) Cell counts were performed with flow cytometry using counting beads, shown relative to a set bead number acquired (n = 5); (E) qPCR analysis of prkcb expression, αKR-SCR (circles) compared with αKR sh-prkcb (triangles). Gapdh was used as the reference gene and αKR-SCR-transduced cells were used as a calibrator (n = 4). All experiments shown are representative of n ≥ 4 biological replicates as indicated. Paired student t-test with Wilcoxon matched-pair signed rank test was used to analyse the data. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.