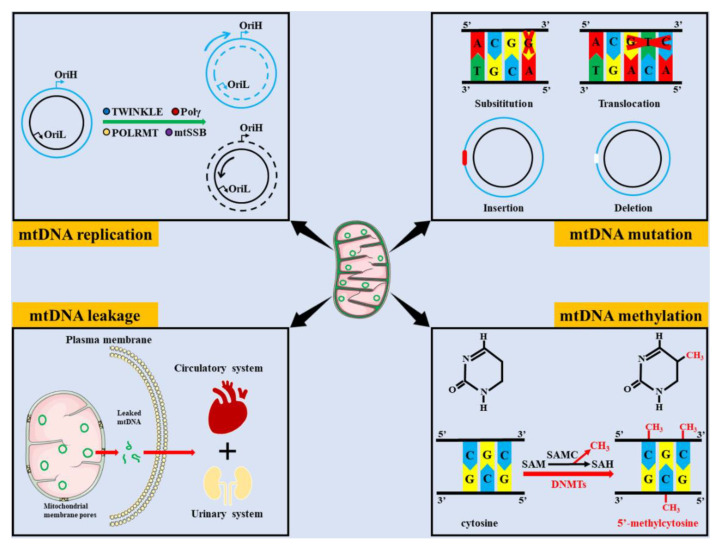
Figure 1.
Common types of mtDNA damage. mtDNA damage includes impaired mtDNA replication, mtDNA mutations, mtDNA leakage and mtDNA methylation. mtDNA replication operates in a semi-conserved manner and contains multiple enzymes, such as TWINKLE, Pol γ, POLRMT, and mtSSB, which may hinder mtDNA replication when they are disrupted. The common types of mtDNA mutation includes substitution, translocation, insertion, and deletion. Leaked mtDNA can be transferred to peripheral plasma and urine via the circulatory and urinary systems, respectively. Under the action of DNMTs, the methyl donor compounds derived from SAM are transferred to CpG islands to form 5′-methylcytosine. (OriH, the origin of heavy strand replication; OriL, the origin of light strand replication; Pol γ, polymerase gamma; POLRMT, mitochondrial RNA polymerase; mtSSB, mitochondrial single-strand binding protein; SAM, S-adenosyl-L-methionine; SAH, S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine; SAMC, S-adenosylmethionine carrier; DNMTs, and DNA methyltransferases).