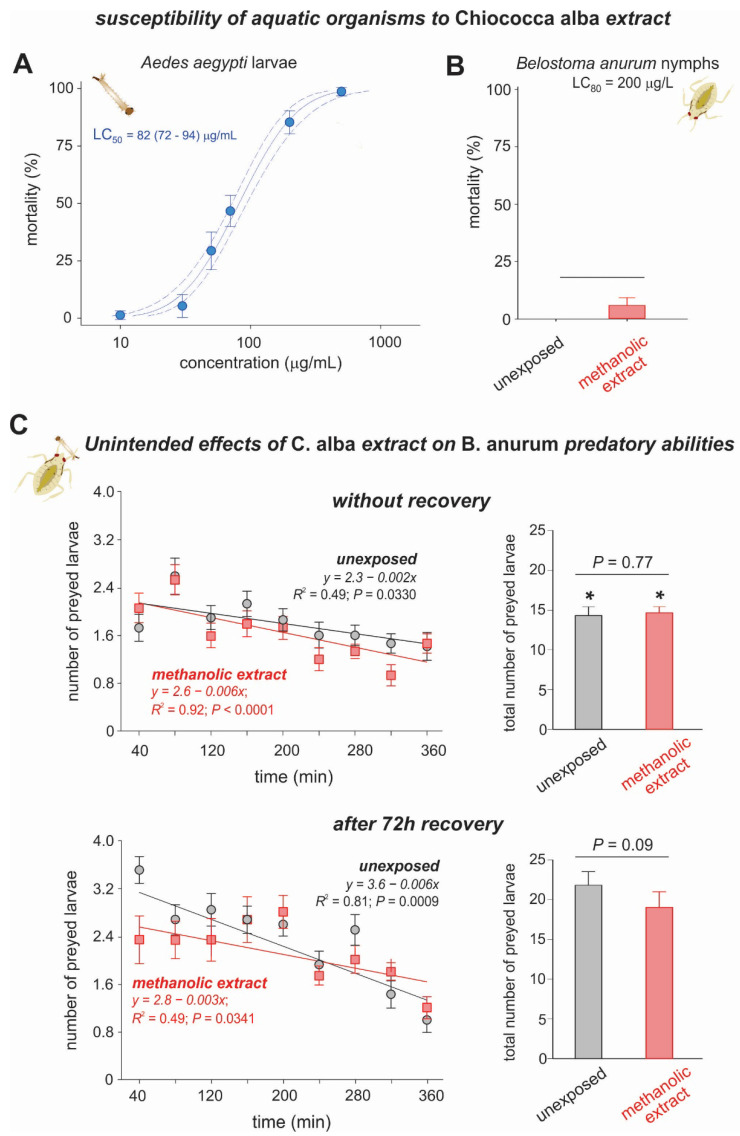
Figure 2.
Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti larvae (A) and Belostoma anurum nymphs (B) to methanolic extracts of Chiococca alba. (C) The number of A. aegypti larvae preyed upon by B. anurum nymphs over time, with and without a period (96 h) of recovery after exposure to the C. alba methanolic extract (200 µg/mL) (left). The total number of A. aegypti larvae preyed upon by B. anurum nymphs (right). The control treatment consisted of unexposed nymphs. (A) A filled circle indicates the mortality values obtained with the extract application, while dotted lines represent the 95% confidence intervals. (B) Data are the mean ± SE. (C) The predatory ability was assessed at the larval density of six larvae/100 mL of water. Larval densities were reestablished after every evaluation. Symbols show the average number of larvae preyed upon by each B. anurum nymph (n = 15). Data are the mean ± SE. * denotes significant differences in the total number of preyed larvae between the two exposure times (i.e., without recovery and after 72 h recovery).