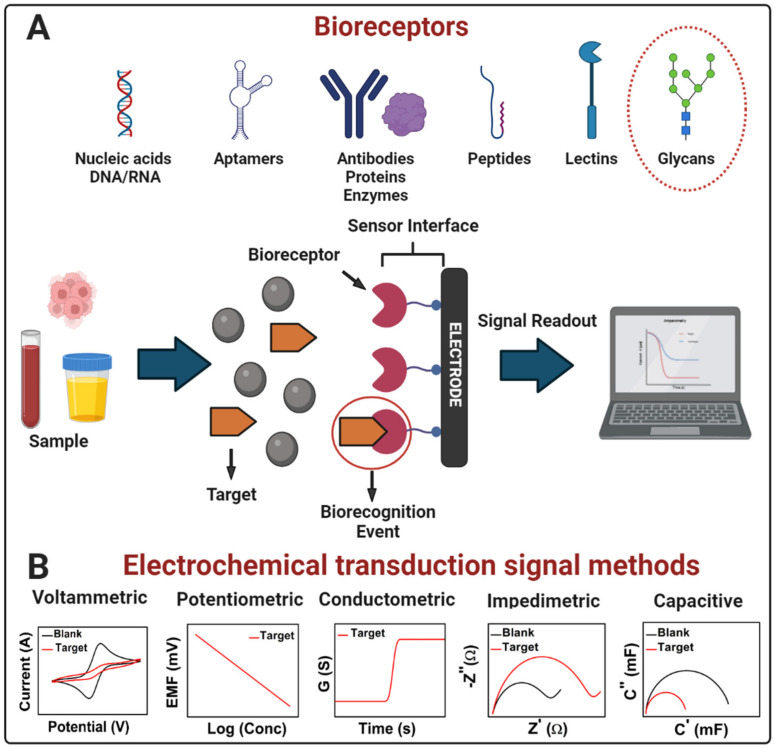
Figure 1.
(A) Scheme of a generic electrochemical biosensor. A bioreceptor (nucleic acids, aptamers, antibodies, proteins, enzymes, peptides, lectins, glycans, etc.) attached to the electrode surface recruits the molecular target (analyte present in a sample) onto the sensor interface by an affinity reaction. After the bioreceptor binding with the target (biorecognition event), the transducer converts the binding event into a measurable signal proportional to the concentration of the target (signal readout). (B) Electrochemical transduction signal methods in biosensors: voltammetric, potentiometric, conductometric, impedimetric, and capacitive. Adapted from [22] with permission. Copyright Elsevier 2022.