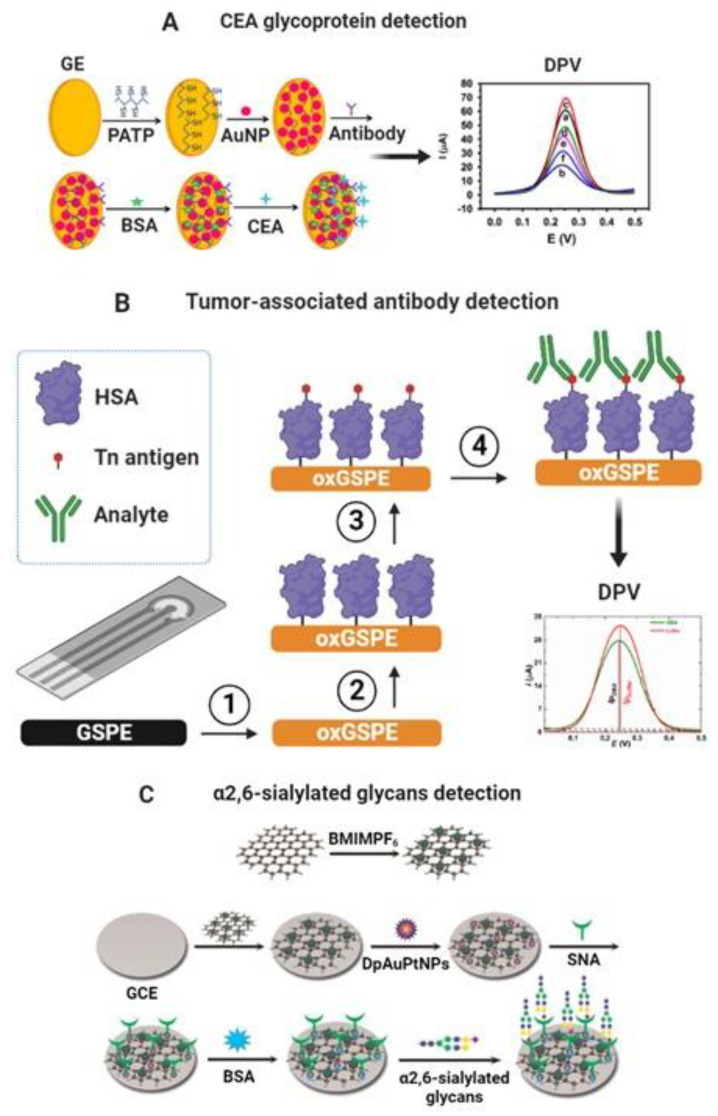
Figure 4.
(A) Scheme of the different steps involved in developing a label-free nanoimmunosensor for CEA detection. (a) Bare gold electrodes and modified with (b) PATP, (c) PATP–AuNPs, (d) PATP–AuNPs–anti-CEA, (e) PATP–AuNPs–anti-CEA blocked with BSA, and (f) PATP–AuNPs–anti-CEA incubated with CEA after being blocked with BSA. Adapted from [98] with permission. Copyright Elsevier 2013. (B) Modification of graphene screen-printed electrode (GSPE) by electrochemical oxidation (step 1), covalent immobilization of human serum albumin (HSA) as a natural nanoscaffold (step 2), and covalent immobilization of a Tn antigen to HSA (step 3). The final step is incubation with the analyte protein (step 4) [135]. (C) Schematic representation of the electrochemical biosensor based on GCE modified with rGO-EPA/BMIMPF6/AuPtNPs. Reproduced from [142] with permission. Copyright Elsevier 2015.