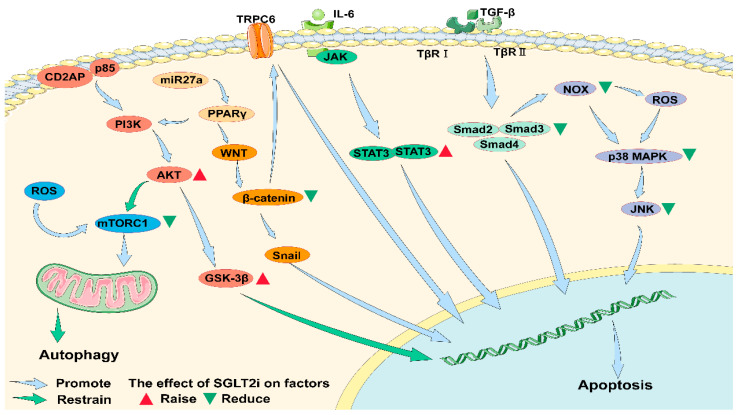
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of promoting apoptosis and resisting apoptosis in podocytes. In DKD, the inflammatory response is enhanced in which ROS attenuate autophagy of podocytes via mTORC1. The combination of CD2AP and p85 promotes the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, which can lead to the apoptosis of podocytes. DKD inhibits the activity of the PI3K/AKT pathway and reduces its activity of inhibiting apoptosis. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is activated in the diabetic state, which activates the downstream effector factor Snail and promotes the apoptosis of podocytes. At the same time, the activation of β-catenin is associated with the activation of the membrane channel TRPC6, which also promotes the apoptosis of foot cells. miR27a can activate the PI3K/AKT pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by mediating PPARγ. The increase of IL-6 in diabetes can activate the JAK/STAT3 pathway, and lead to apoptosis of podocytes. At the same time, the increased TGF-β can promote the activation of TβRI and TβRII and then promote the activity of Smad family. This pathway can also lead to podocyte autophagy. In addition, NOX can promote p38/MAPK pathway through ROS or directly, activate JNK downstream and promote podocyte autophagy. SGLT2i may exert effects on all the above pathways. Studies have shown that the use of SGLT2i can reduce the activity of mTORC1 in cells and promote autophagy. In addition, the use of SGLT2i can enhance the expression of AKT, reduce the expression of β-catenin and Smad families and inhibit the p38/MAPK/JNK pathway to inhibit apoptosis. However, studies have also shown that SGLT2i can promote the expression of STAT3 and thus promote apoptosis. ROS: reactive oxygen species; mTORC1: molecular target of rapamycin complex 1; CD2AP: CD2-associated protein; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; AKT: protein kinase B; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3 β; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; TRPC6: transient receptor potential cation channel, subclass C, member 6; IL-6: interleukin-6; JAK: janus kinase; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta; TβRI: the transformation growth factor-β type I receptor kinase domain; TβRII: the transformation growth factor-β type II receptor kinase domain; Smad: the drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein; NOX: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK: c-JunN-terminal kinase.