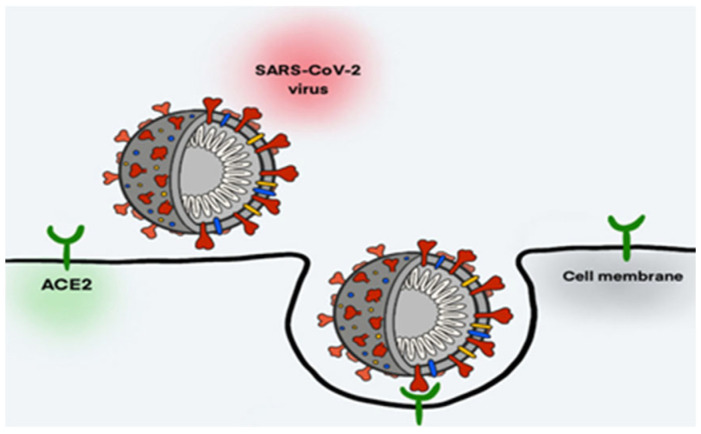
Figure 1.
Diagram of SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cell. The spike glycoprotein (red), which consists of two subunits, binds to the ACE2 receptor (green) of host cells to merge the viral and cellular membranes and insert the viral genomic RNA (white) into the host cell. This induces endocytosis and the merging of the viral and cellular membranes, causing the viral genomic RNA to be inserted into the host cell, and thus, allowing the virus to replicate. The binding of SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2 receptor causes a downregulation of this receptor, disrupting its normal function in maintaining immune homeostasis and leading to pro-inflammatory effects that can cause lung injury. The figure was reproduced from [8] (Atzrodt CL et al., 2020).