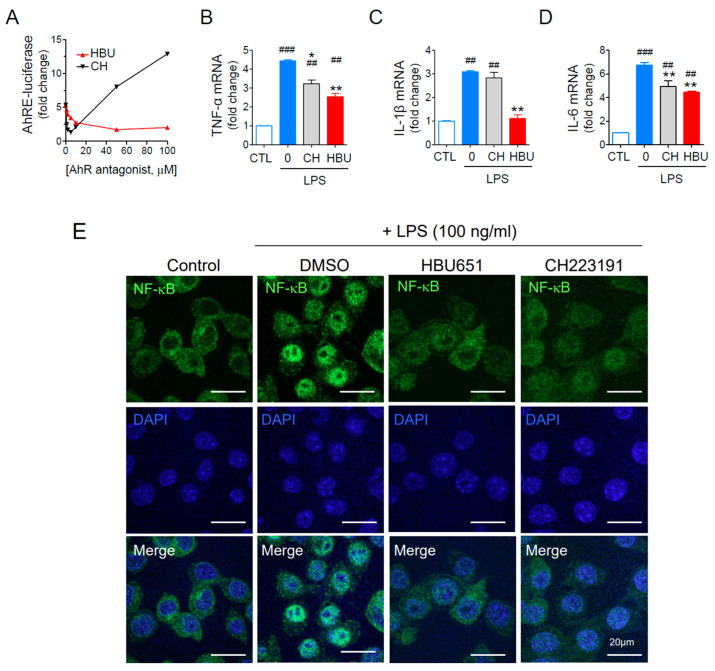
Figure 1.
Effects of AhR antagonists on inflammatory cytokines and mitochondrial activities. (A) Dose-dependent AhR antagonist activity assay using AhR-dependent luciferase (AhRE-luciferase) assay. The cells were pretreated with AhR antagonists for 1 h, stimulated with 50 pM TCDD for 24 h, and assayed for luciferase activity. (B–D) Murine BV2 microglial cells were pre-treated with 10 μM HBU651 (HBU) or 1 μM CH223191 (CH) for 24 h, stimulated with 100 ng/mL LPS for 4 h, and harvested for analysis. Realtime qRT-PCR for TNF-α (B), IL-1β (C), and IL-6 (D) mRNA levels. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 5). ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. Control (CTL), and * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. LPS-treated DMSO. (E) Effect of HBU651 on LPS-induced nuclear localization of NF-κB. Murine BV2 microglial cells were pre-treated with 10 μM HBU651 or 1 μM CH223191 for 24 h, prior to 100 ng/mL LPS stimulation for 4 h. BV2 cells were immunostained with NF-κB p65/RELA antibody (green) and DAPI (blue) for nuclei (Merge). Cell images were enlarged to visualize the nuclear localization of NF-κB (Enlarged). Representative confocal micrograph images of BV2 cells are shown (scale bar = 20 μm).