FIGURE 5.
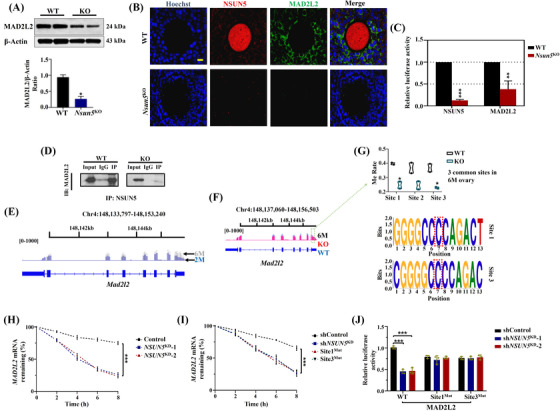
Nsun5 affected oocyte function by inhibiting the m5C modification of Mad2l2. (B and C) Relative luciferase activity of Hoechst (blue), NSUN5 (red) and MAD2L2 (green) in the Nsun5 KO and WT groups (*p < .05, **p < .01). (A) Protein expression of MAD2L2 in the Nsun5 KO and WT groups (*p < .05). (D) Co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) showing the interaction between NSUN5 and MAD2L2. (E) Representative m5C sites of Mad2l2 on chromosome 4 in the WT group. (F) Representative m5C sites of Mad2l2 on chromosome 4 at 6 months in the Nsun5KO and WT groups. (G) Differential methylation rates of two common m5C sites at 6 months (*p < .05). (H) MAD2L2 mRNA stability of NSUN5 KD and control KGN cells (***p < .001). (I) mRNA stability of MAD2L2 in the control, NSUN5 KD, site 1Mut and site 3Mut groups (***p < .001). (J) Luciferase expression of MAD2L2‐WT, MAD2L2‐site 1Mut and MAD2L2‐site 3Mut in the control and NSUN5 KD cell lines (***p < .001)
