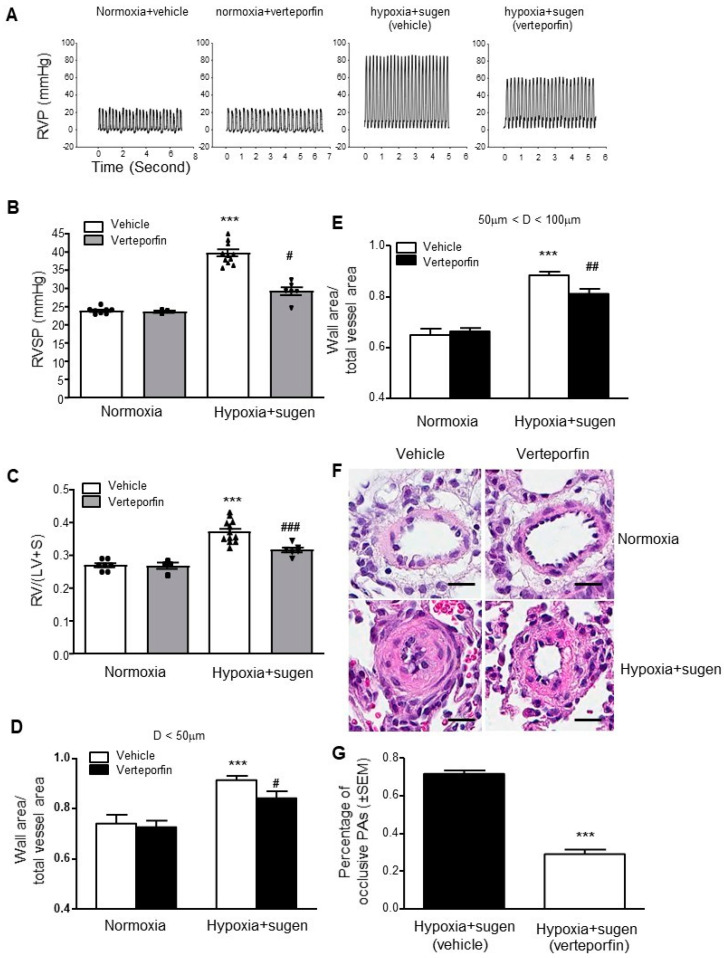
Figure 11.
YAP inhibition with verteporfin attenuates hypoxia-plus-Sugen-mediated pulmonary hypertension in rats. Compared with the controls, verteporfin treatment attenuated the development of pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH), as assessed by changes in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), right ventricular hypertrophy (RV/LV+S), and the development of medial hypertrophy and neointima formation. (A) Representative record of right ventricular pressure (RVP) tracings; (B) changes in RVSP; (C) changes in RV/(LV + S); (D) changes in ratios of wall area to total vessel area of pulmonary arteries less than 50 μm in diameter in the lung sections of the control and verteporfin-treated groups; (E) changes in ratios of wall area to total vessel area of pulmonary arteries 50–100 μm in diameter in the lung sections of the control and verteporfin-treated groups; (F) representative pulmonary artery images in the lung sections of control and verteporfin treated groups; (G) percentage of occlusive PAs significantly decreases with verteporfin therapy. Scale bar: 20 μm. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; number of rats in each group (n = 4–10) is shown in panels B and C. *** p < 0.001 versus normoxia without verteporfin group (B–E) or hypoxia without verteporfin group (G); # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01; ### p < 0.001 versus hypoxia without verteporfin group.