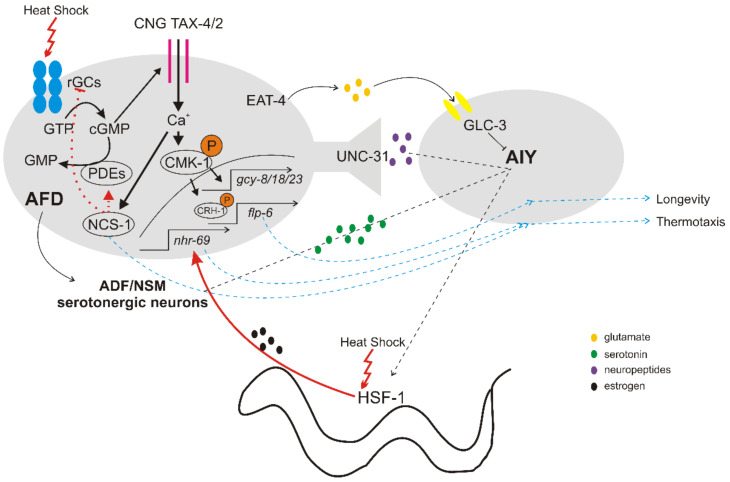
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of AFD/AIY thermosensory circuit signaling. Temperature rising is received in AFD sensory neurons by rGCs that upregulate cGMP concentration. This leads to the opening of the CNG TAX-4/TAX-2 channels and the release of a calcium influx, resulting in depolarization of AFD membrane potential. The calcium influx maintains cGMP concentration levels through NCS-1 and further upregulates rGCs via CMK-1 phosphorylation. Phosphorylated CMK-1 enters the nucleus and among regulation of rGCs expression levels, also participates in CRH-1 phosphorylation and subsequent FLP-6 activation that is responsible for normal longevity under elevated temperatures. AFD activation leads to both excitatory and inhibitory signal transmission on AIY interneuron possibly by UNC-31-mediated peptides release and by glutamate release, accordingly. This activation can also release serotonin from serotonergic neurons and upregulate HSF-1 through AIY in the intestine. These signals are necessary for AIY to promote thermal behaviors (thermotaxis) and activate HSF-1-related organismal thermal responses in somatic tissues. In succession, HSF-1 can also signal to AFD in part through estrogen signaling to ensure normal thermotaxis.