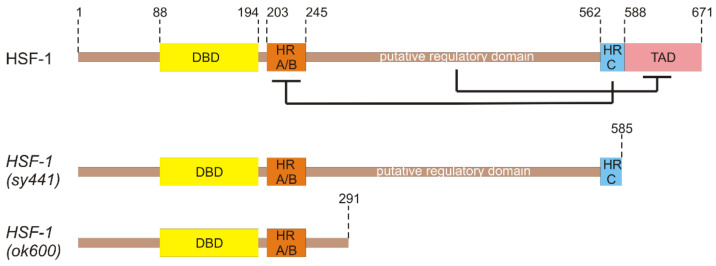
Figure 2.
Domain structure of C. elegans HSF-1 full-length protein and the truncated alleles sy441 and ok600. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. DBD is the DNA-binding domain, HR-A/B and HR-C are the trimerization domains and TAD is the transactivation domain. HSF-1 trimerization is negatively regulated by intramolecular interactions between the HR-A/B and the HR-C domains. The exact position of the regulatory domain in the C. elegans HSF-1 is not yet determined. However, it is most possibly located between the two trimerization domains and negatively regulates the trans-activating capacity of HSF-1. sy441 allele is lacking the transactivation domain, while ok600 allele is lacking both TAD and the putative regulatory domain.