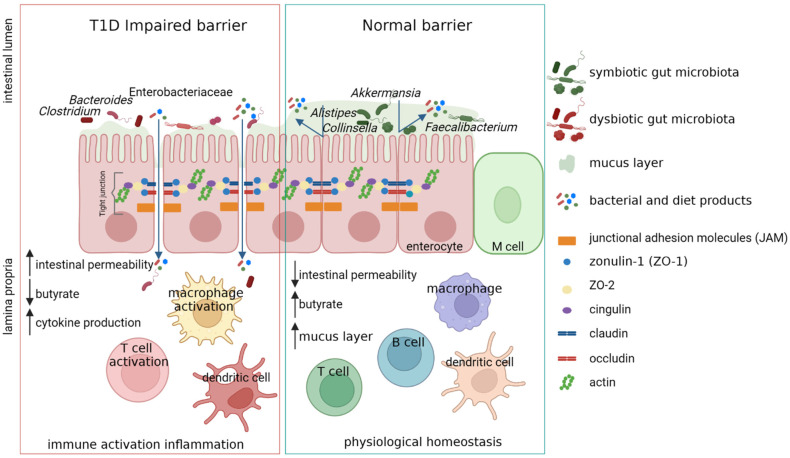
Figure 1.
Increasing gut paracellular permeability in T1D patients. The alteration of tight junction (TJ) proteins leads to the increase of intestinal permeability, providing access to the lamina propria environment for foreign agents (e.g., bacteria and bacterial and diet products). The accumulation of these bacteria and molecules can trigger inflammation pathways, causing intestinal inflammation. The activated and expanded T-cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) could travel via mesenteric and pancreatic lymph nodes to the pancreas and induce T1D. Created with BioRender.com.