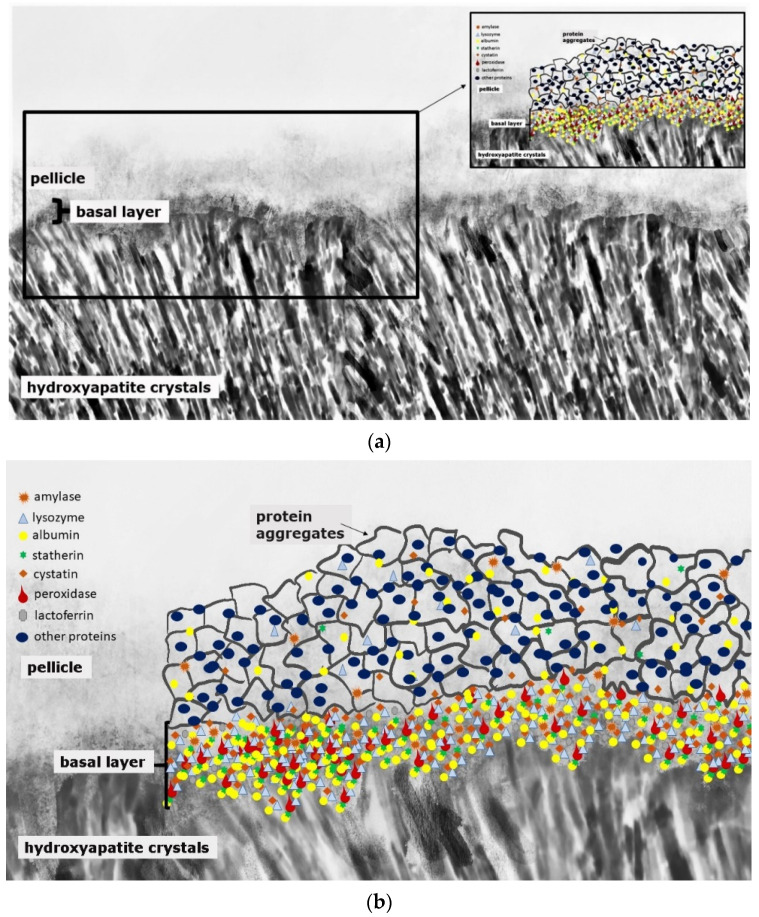
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the acquired enamel pellicle (a,b). The primary basal pellicle layer consists of pellicle precursor proteins such as statherin, histatin, acidic proline-rich proteins (PRP), mucins, amylase, cystatin, peroxidase, lysozyme and lactoferrin (b). After the formation of this dense protein network of the basal layer, the pellicle maturation process is characterized by the adhesion of 100–200 nm sized protein aggregates and peptide complexes (b).