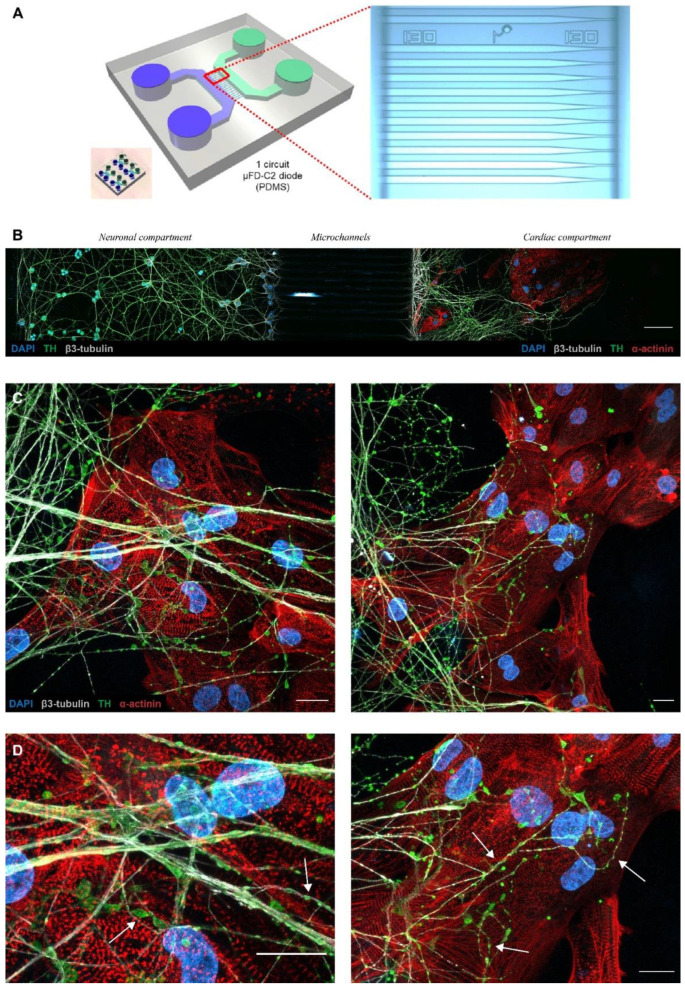
Figure 2.
Neuronal diodes fluidic microsystems as tools to establish compartmentalized neurocardiac co-culture on chip. (A) Structural characteristics of a two-chamber neuronal diode also known as Brainies®. Left panel: 3D model of the micro-structured PDMS-based block (grey), including cylindric wells (diameter: 4 mm; height: 5 mm), rectangular cell culture chambers (vol. ~1 µL; height: 55 µm), and a series of asymmetrical microchannels (length: 500 µm; height: 3 µm; width: tapering from 15 µm to 3 µm). The compartment where neurons are seeded is represented in blue and the compartment where cardiomyocytes are seeded is represented in green. The small insert shows a picture of one of the Brainies® that contains four neuronal diodes. Right panel: micro-graph of a portion of the funnel-shaped microchannels. (B) In this fluorescence microscopy image of a microfluidic chip section, the neural compartment is located to the left and the cardiac compartment to the right. Between the two compartments are the microchannels (not visible in the image, scale bar: 100 µm). PC12 cells differentiate directly into their compartments and their axons project into the cardiac compartment through the channels. (C,D) Images of neuro–cardiac interactions in cardiac compartments after 14 days of co-culture. Tyrosine hydroxylase (in Green) appear apposed along axons. Axons (β3-tubulin; in white) harbor varicosities in the interaction zones (white arrows). (Blue: DAPI, Red: sarcomeric α-actinin, green: Tyrosine hydroxylase, white: β3-tubulin, scale bar: 20 µm).