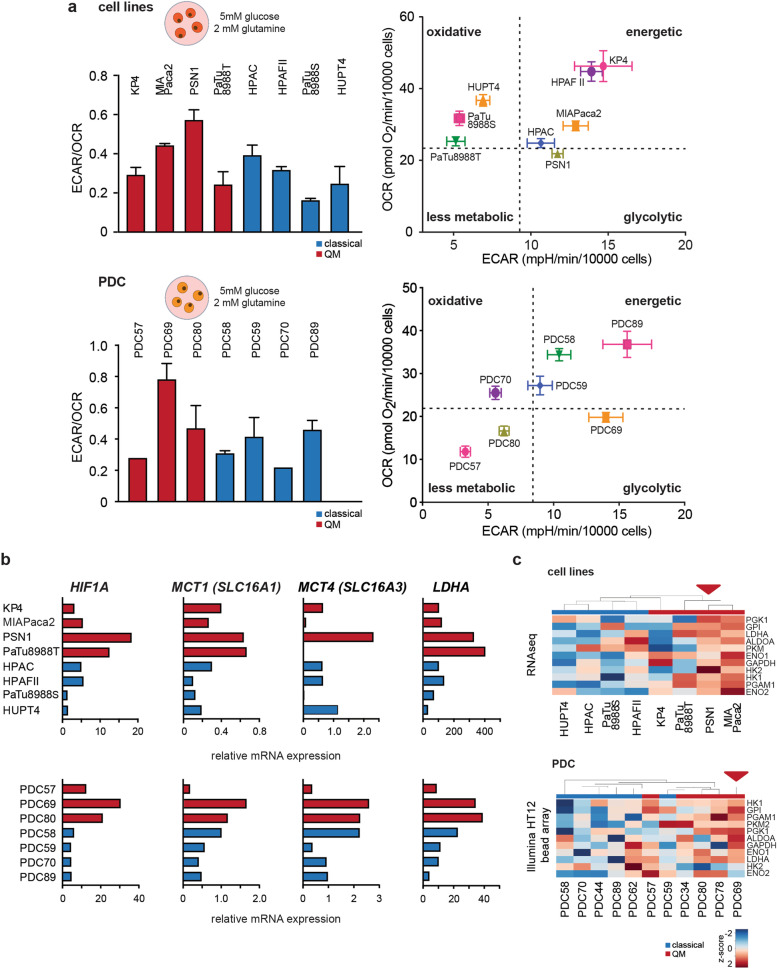
Fig. 2.
Functional glycolysis evaluation in PDAC cells. a ECAR to OCR ratios (ECAR/OCR) and energy maps as measured by seahorse metabolic flux assay for PDAC cell lines (upper) and PDCs (lower) in medium supplemented with 5 mM glucose (physiological concentration) and 2 mM glutamine. Higher ECAR/OCR ratio indicates higher glycolysis in PSN1 and PDC69 cells under these conditions. Presented are mean + SD values calculated from 2 independent experiments, with at least 5 technical replicates per cell line per experiment. Energy maps (OCR vs ECAR plots) show glycolytic energetic positioning of PSN1 and PDC69 cells. Representative energy maps from one experiment, at least 5 technical replicates per cell line. At least 2 independent experiments performed. OCR and ECAR values were normalized to 10,000 post-experimentally counted, viable cells. Dotted lines present arbitrary cutoff levels used for separation of different energy phenotypes (glycolytic, oxidative, energetic, or less metabolic). b Relative gene expression (qPCR) data for LDHA, MCT1 (SLC16A1), MCT4 (SLC16A3), and HIF1a in cell lines and PDCs. High gene expression levels were observed for PSN1 and PDC69 (both QM subtype). Beta-glucuronidase (GUSB) expression was used as house-keeper control. c Hierarchical clustering analysis for glycolytic genes using gene expression data for cell lines (RNA-seq) and PDCs (HT12 Illumina gene expression array). Z-score: red color—high expression, blue color—low expression. PSN1 and PDC69 show higher expression of investigated glycolytic genes