Figure 1.
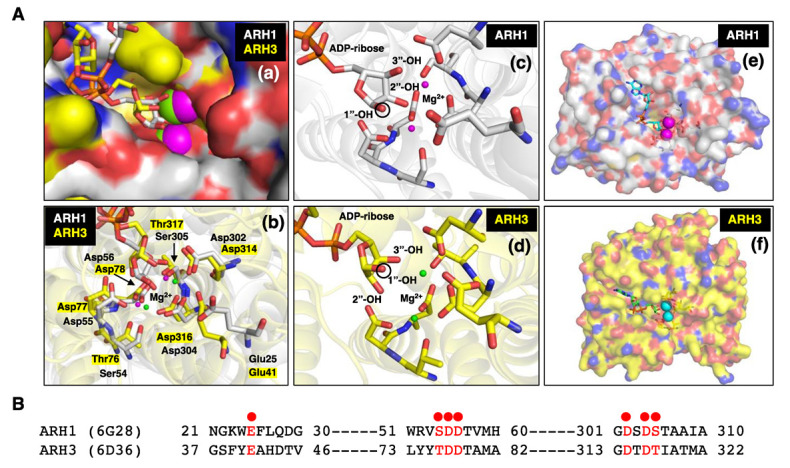
(A) (a) Close-up surface representation of human ARH1 (white, PDB ID: 6g28) [98] and ARH3 (yellow, PDB ID: 6d36) [99] crystal structures with electro-negative (red) and -positive atoms (blue). The binding pocket of ADP-ribose on surface of ARH1 and ARH3 is near the bound Mg2+ ions (magenta-ARH1, green-ARH3) [23,76,98,99,100]. (b) Crystal structure of ARH1 and ARH3 with ADP-ribose and Mg2+ ions (ARH1-magenta, ARH3-green). Glu25, Ser54, Asp55, Asp56, Asp302, Asp304, and Ser305 in ARH1, and Glu41, Thr76, Asp77, Asp78, Asp314, Asp316, and Thr317 in ARH3 (yellow highlight) hydrogen-bonding amino residues near Mg2+ are critical for binding of ADP-ribose, and ARH1 and ARH3 hydrolase activities. (c,d) Close-up two Mg2+ ions and ADP-ribose in binding pocket of ARH1 (c) and ARH3 (d). The black circle on ribose indicates the 1”-OH of ribose that is an attachment site of arginine or serine residue of modified protein, O-acetyl or nicotinamide of α-NAD+ [28]. (e,f) Surface representation of human ARH1 (white, PDB ID: 6g28) and ARH3 (yellow, PDB ID: 6d36) crystal structures. ADP-ribose (cyan-ARH1, green-ARH3) and Mg2+ ions (magenta-ARH1, cyan-ARH3) are bound in the pocket of ARH1 or ARH3. (B) Structure-guided alignment of selected ARH1 and ARH3 protein residues (red dot) bound with Mg2+ ions. Crystal structures of ARH1 (PDB ID: 6g28) and ARH3 (PDB ID: 6d36) with bound ADP-ribose and magnesium were taken from the Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org, accessed on 13 October 2022). Figures and structure analysis were created with Pymol (http://pymolorg, accessed on 13 October 2022).
