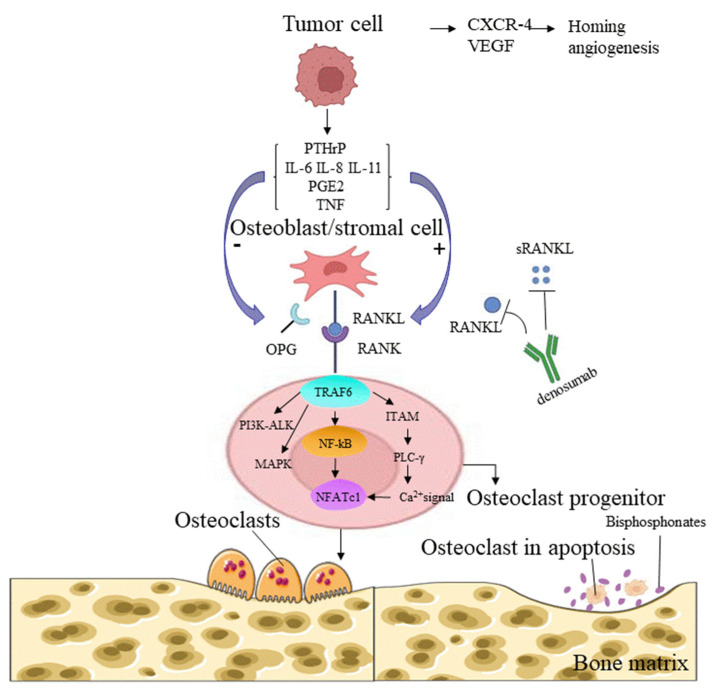
Figure 2.
RANKL-RANK signaling in osteolytic bone metastases. Tumor cells arriving in the bone marrow microenvironment secrete tumor-related factors, such as CXCR-4 and VEGF, to promote the colonization and survival of tumor cells in the bone marrow, and PTHrP, IL-6, IL-8, IL-11, PGE2, and TNF stimulate osteoblasts and stromal cells to produce RANKL, which binds to the RANK expressed on osteoclasts. The interaction of RANKL and RANK promotes osteoclast survival and differentiation, and mature osteoclasts eventually cause bone resorption. Osteoblasts also produce OPG, which inhibits bone resorption by competing with RANK to bind to RANKL. The binding of the human monoclonal antibody denosumab to RANKL inhibits bone destruction, by blocking the RANKL-RANK axis. Bisphosphonates inhibit osteoclast activity and the growth of tumor cells, and exert an osteoprotective effect [121]. CXCR-4 = chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; PTHrP = parathyroid hormonerelated peptide; IL-6 = interleukin-6; IL-8 = interleukin-8; IL-11 = interleukin-11; PGE2 = prostaglandin E2; TNF = tumor necrosis factor; RANKL = receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand; RANK = receptor activator of NF-kappa B; OPG = osteoprotegerin.