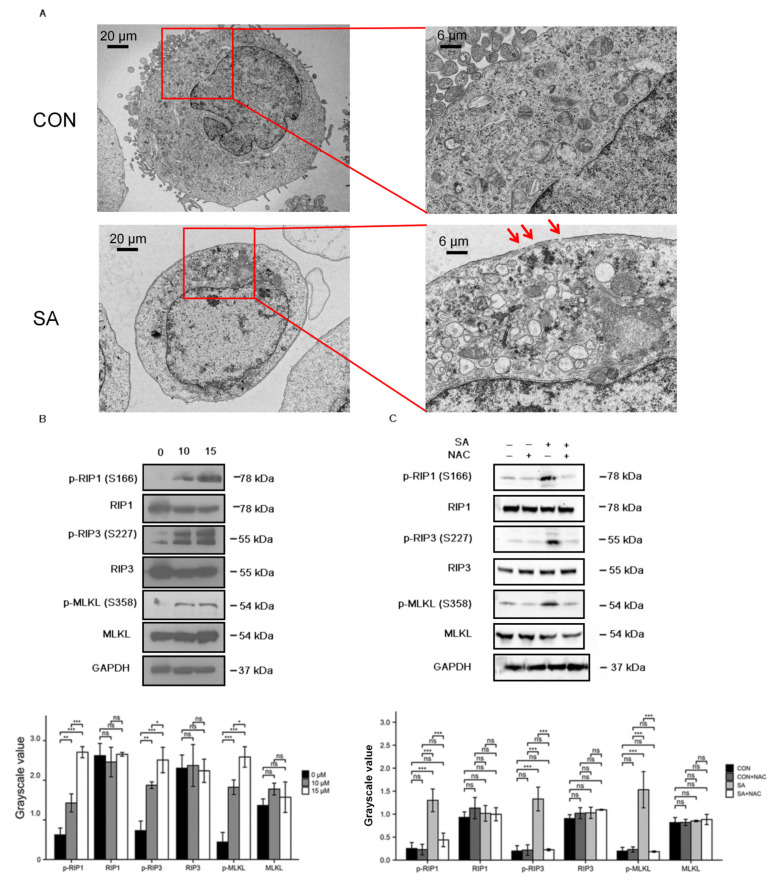
Figure 4.
Scabertopin-treated J82 cells undergo necroptosis, which can be rescued by NAC. (A) TEM images are shown for the control group (CON) and the J82 cells treated with 10 μM of scabertopin (SA) for 24 h. The image on the right is an enlarged image of the left image, and the red arrow points to the perforation on the cell membrane during necroptosis; at least three independent samples were observed in each group. (B) Scabertopin can significantly increase the phosphorylation of the necroptosis-related proteins RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL (n = 3) after 24 h of treatment; (C) Scabertopin-induced phosphorylation of RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL can be reversed by NAC in the group treated with 10 μM of scabertopin for 24 h. A total of 5 μM of NAC was used in the experiments. The grayscale values are normalized to GAPDH. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. of the three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns: no significance vs. 0 μM scabertopin-treated group. MLKL: mixed lineage kinase like; NAC: N-acetylcysteine; p-: phosphorylated; RIP1: receptor-interacting protein.