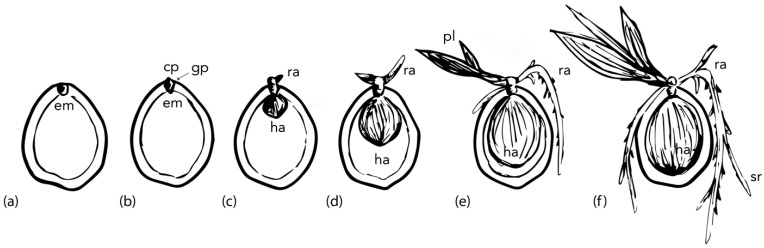
Figure 4.
Coconut germination stages: (a) Ungerminated coconut fruit. Embryo (em) consists of a short plumular-radicular axis. The plumule consists of a central meristematic zone enclosed by scaly-leaf primordia, which are then surrounded by the cotyledonary petiole. (b) In the proximal end of the embryo, the cotyledonary petiole (cp) extends through the germination pore (gp). (c) Germinative button formation and radicle emergence (ra) from the cotyledonary petiole. The cotyledonary blade (distal end of the embryo) starts expanding to form a haustorium (ha). (d) Radicle elongation, plumule emergence and continuous haustorium growth. (e) Secondary roots forming, plumule elongation and first leaves, extensive haustorium growth. (f) Secondary root (sr) growth, leaf growth, haustorium completely fills the inner cavity (endosperm).