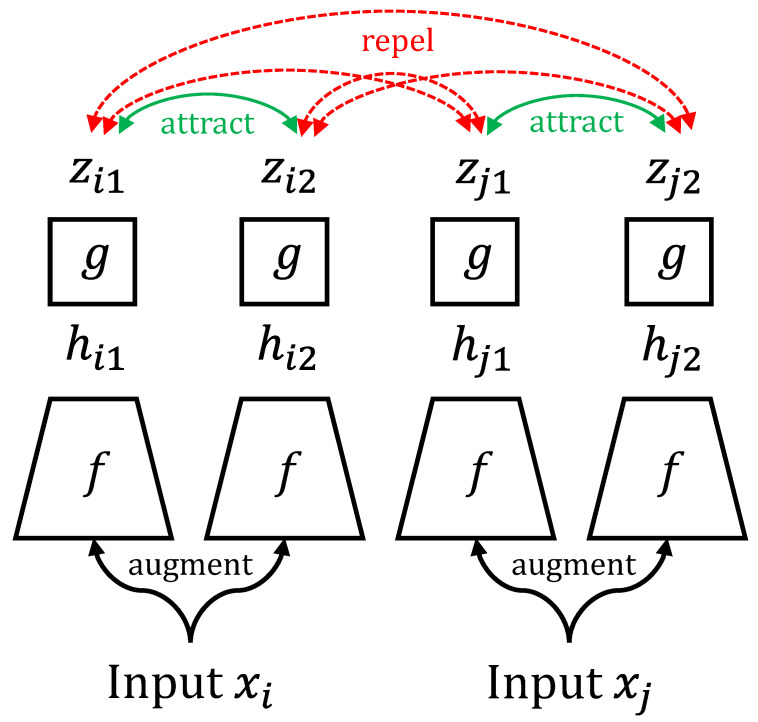
Figure 1.
Contrastive learning as presented in SimCLR [39]. The input images xi and xj are augmented via random transformations, embedded via encoder f to yield embedding h, and then projected via g to yield projection z. The contrastive objective maximizes the similarity between positive pair zi1 and zi2 as well as positive pair zj1 and zj2 (i.e., “attract”) while minimizing the similarity between all other (negative) pairs (i.e., repel).