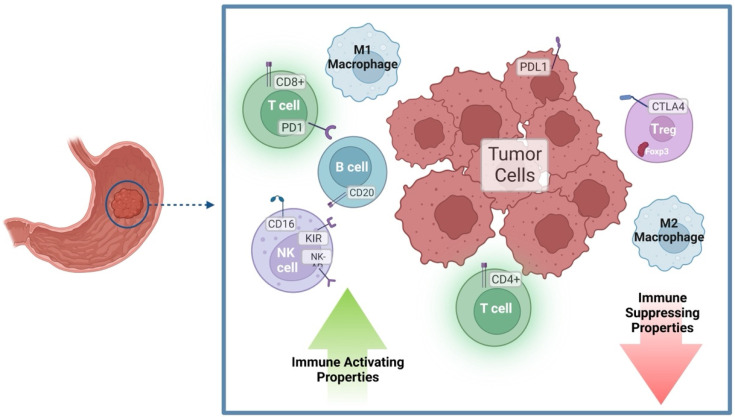
Figure 1.
Infiltrating immune cells balance the inflammatory vs. immuno-suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) in GC. CD8+ T cells are generally cytotoxic to tumor cells, although the tumor may evade the immune system via PD-1/PD-L-1 signaling. CD4+ T cells may differentiate into T helper subtypes with pro-inflammatory properties. However, differentiation into Treg with CTLA4 expression will drive an inhibition of immune cell activity. B cells are generally thought to have anti-tumor immune activating functions. M1 macrophages are pro-inflammatory and drive immune activation in the TME, while M2 macrophages decrease immune responses. NK cells may have anti-tumor properties which can be inhibited by tumor-secreted factors. Figure created with BioRender.com (accessed on 25 October 2022).