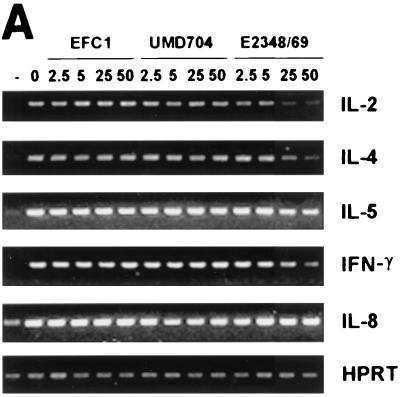
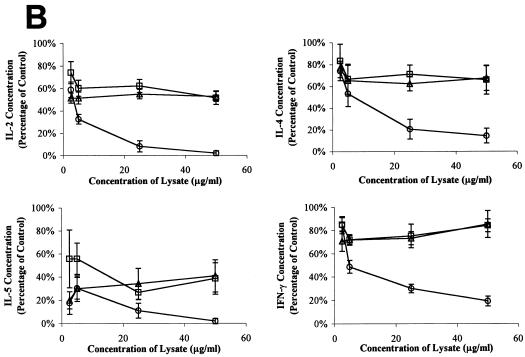
FIG. 2.
Lymphostatin is required for EPEC-mediated inhibition of lymphokine expression by PBMC. (A) Effect of bacterial lysates on lymphokine mRNA expression. PBMC were incubated in the absence of bacterial lysates and were left unstimulated (−) or exposed to 0, 2.5, 5, 25, or 50 μg/ml of bacterial lysates from commensal E. coli EFC1, lifA mutant EPEC strain UMD704, or wild-type EPEC stain E2348/69 as indicated and were stimulated with PMA-PWM. Expression of IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, gamma interferon (IFN-γ), IL-8, and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase mRNA were assessed by reverse transcription-PCR. (B) Effect of bacterial lysates on lymphokine protein expression. PBMC were incubated with lysates from wild-type EPEC strain E2348/69 (circles), EPEC lifA mutant UMD704 (squares), or commensal E. coli EFC1 (triangles) and were stimulated as indicated in the legend to panel A. Values were calculated as described in Materials and Methods as percentages of concentrations measured in cells stimulated in the absence of lysates and are pooled from duplicate values of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard errors of the means (SEMs). The absolute mean values (± SEMs) for cells stimulated in the absence of lysates were 4.38 ± 1.18 ng/ml for IL-2, 37.2 ± 4.8 pg/ml for IL-4, 99.7 ± 34.6 pg/ml for IL-5, and 1.84 ± 0.25 ng/ml for gamma interferon.