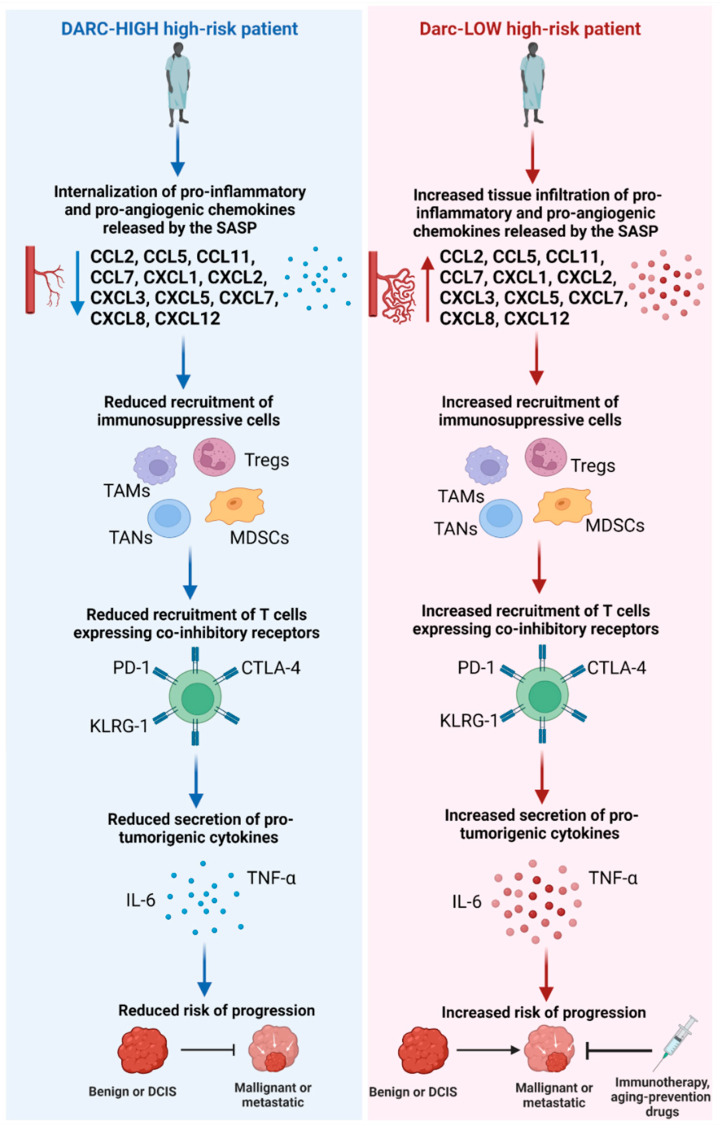
Figure 1.
Potential role of DARC expression in influencing risk of inflamm-aging-mediated progression among high-risk patients. Illustration of how endothelial or epithelial DARC IHC expression levels may be influencing risk of progression among patients with high-risk lesions. High-risk patients with low DARC IHC expression may exhibit increased tissue infiltration of pro-tumorigenic cytokines and chemokines, immunosuppressive cells and T cells expressing co-inhibitory molecules, which can increase likelihood for neoplastic transformation and progression to occur. Early-stage immunotherapeutic or age-prevention drug intervention based on DARC status could potentially derail progression to malignancy or metastatic breast cancer.