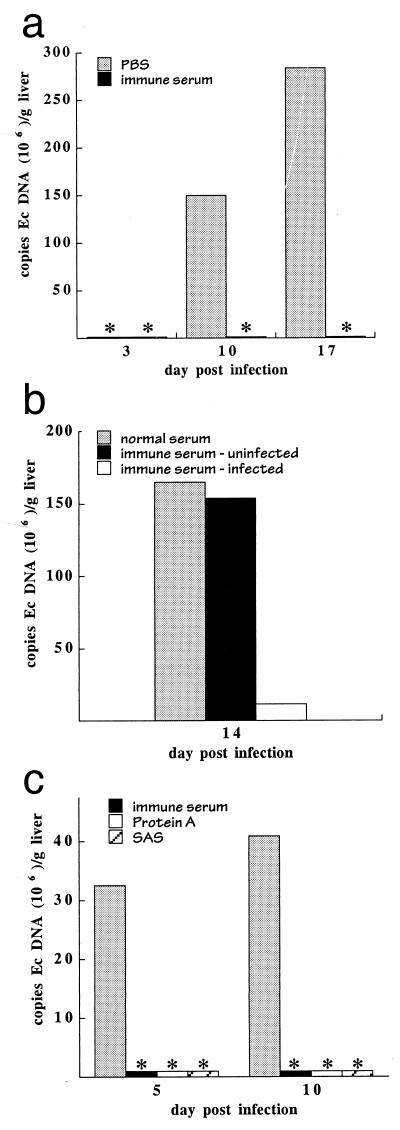
FIG. 2.
Bacterial clearance was E. chaffeensis specific and was mediated by antibodies. (a) C57BL/6 scid mice were infected by transfer of E. chaffeensis-infected splenocytes obtained from a SCID mouse 17 days postinfection. Immune serum was obtained from C57BL/6 mice that had been inoculated with E. chaffeensis-infected DH82 cells and was administered at the time of bacterial infection. Bacterial loads were determined by QPCR. ∗, bacteria were not detected in the infected mice. Each histogram bar represents a single mouse. Ec, E. chaffeensis. (b) Mice were infected as described for Fig. 1 and were administered on day 10 postinfection normal mouse serum or serum obtained from C57BL/6 mice that had been inoculated with either uninfected DH82 cells (immune serum-uninfected) or with E. chaffeensis-infected DH82 cells (immune serum-infected). Liver tissue was harvested on day 14 for QPCR analyses. QPCR analyses of representative individual mice are shown. The observations were confirmed in a separate experiment (not shown) where 16 mice (in three groups) were analyzed over a period of 24 days. The semiquantitative data from both experiments where serum was administered on day 14 postinfection were normalized and combined (a total of four mice for each group), and the means and standard deviations were as follows: normal serum, 5.0 ± 0.82; serum from mice inoculated with uninfected cells, 4.3 ± 1.1; immune serum, 1.8 ± 1.8. (c) C57BL/6 scid mice were infected on day 0 with E. chaffeensis-infected DH82 cells, followed by intraperitoneal administration of 0.1 ml of PBS or C57BL/6 immune serum, 200 μg of ammonium sulfate-fractionated immune serum (SAS), or 100 μg of protein A affinity-purified antibodies 3 days postinfection. The presence of E. chaffeensis antibodies in each of the preparations was confirmed by immunofluorescence assay. Mice were harvested 5 and 10 days postinfection, and liver tissue from representative individual mice was analyzed by QPCR. Semiquantitative analyses of a total of 16 mice from two experiments revealed significant differences between the buffer- and antibody-treated mice (mean ± standard deviation): PBS, 3.8 ± 0.83; immune serum, 1.0 ± 1.2; protein A-purified antibodies, 0.5 ± 0.87; ammonium sulfate-purified antibodies, 1.3 ± 1.3. ∗, bacteria were not detected in the QPCR assays.